Product Description
Model Selection
ZD Leader has a wide range of micro motor production lines in the industry, including DC Motor, AC Motor, Brushless Motor, Planetary Gear Motor, Drum Motor, Planetary Gearbox, RV Reducer and Harmonic Gearbox etc. Through technical innovation and customization, we help you create outstanding application systems and provide flexible solutions for various industrial automation situations.
• Model Selection
Our professional sales representive and technical team will choose the right model and transmission solutions for your usage depend on your specific parameters.
• Drawing Request
If you need more product parameters, catalogues, CAD or 3D drawings, please contact us.
• On Your Need
We can modify standard products or customize them to meet your specific needs.
Product Parameters
Planetary Gear Motor
| MOTOR FRAME SIZE | 32 mm / 42mm / 52mm / 62mm / 72mm / 82mm / 105mm / 120mm |
| MOTOR TYPE | Brush or Brushless |
| OUTPUT POWER | 10W / 15W / 25W / 40W / 60W / 90W / 120 W / 140W / 180W / 200W / 300W(Can Be Customized) |
| OUTPUT SHAFT | 8mm / 10mm / 12mm / 15mm ; Round Shaft, D-Cut Shaft, Key-Way Shaft (Can Be Customized) |
| Voltage type | 12V,24V,48V |
| Accessories | Electric Brake / Encoder |
| GEARBOX FRAME SIZE | 32 mm / 42mm / 52mm / 62mm /72mm/82mm |
| Gear Ratio | 3.65K-392.98K |
| Type Of Pinion | GN Type / GU Type |
Type Of Planetary Gear Motor
Other Products
Company Profile
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Type: | Z2 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors handle variations in brake torque and response time?
Brake motors are designed to handle variations in brake torque and response time to ensure reliable and efficient braking performance. These variations can arise due to different operating conditions, load characteristics, or specific application requirements. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors handle variations in brake torque and response time:
- Brake Design and Construction: The design and construction of brake systems in brake motors play a crucial role in handling variations in brake torque and response time. Brake systems typically consist of brake pads or shoes that press against a brake disc or drum to generate frictional forces and provide braking action. The materials used for the brake components, such as brake linings, can be selected or designed to offer a wide range of torque capacities and response characteristics. By choosing the appropriate materials and optimizing the brake system design, brake motors can accommodate variations in torque requirements and response times.
- Brake Control Mechanisms: Brake motors employ different control mechanisms to manage brake torque and response time. These mechanisms can be mechanical, electrical, or a combination of both. Mechanical control mechanisms often utilize springs or levers to apply and release the brake, while electrical control mechanisms rely on electromagnets or solenoids to engage or disengage the brake. The control mechanisms can be adjusted or configured to modulate the brake torque and response time based on the specific needs of the application.
- Brake Torque Adjustments: Brake motors may offer provisions for adjusting the brake torque to accommodate variations in load requirements. This can be achieved through the selection of different brake linings or by adjusting the spring tension or magnetic force within the brake system. By modifying the brake torque, brake motors can provide the necessary braking force to meet the demands of different operating conditions or load characteristics.
- Response Time Optimization: Brake motors can be engineered to optimize the response time of the braking system. The response time refers to the time it takes for the brake to engage or disengage once the control signal is applied. Several factors can influence the response time, including the design of the control mechanism, the characteristics of the brake linings, and the braking system's overall dynamics. By fine-tuning these factors, brake motors can achieve faster or slower response times as required by the application, ensuring effective and timely braking action.
- Electronic Control Systems: In modern brake motors, electronic control systems are often employed to enhance the flexibility and precision of brake torque and response time adjustments. These systems utilize sensors, feedback mechanisms, and advanced control algorithms to monitor and regulate the brake performance. Electronic control allows for real-time adjustments and precise control of the brake torque and response time, making brake motors more adaptable to variations in operating conditions and load requirements.
By combining appropriate brake design and construction, control mechanisms, torque adjustments, response time optimization, and electronic control systems, brake motors can effectively handle variations in brake torque and response time. This enables them to provide reliable and efficient braking performance across a wide range of operating conditions, load characteristics, and application requirements.
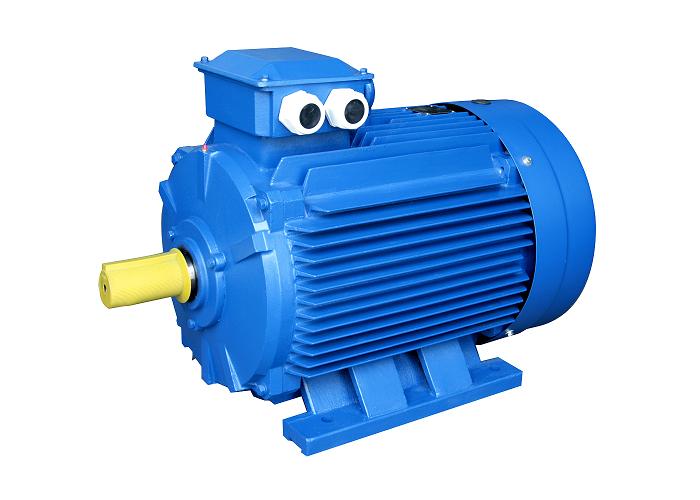

Can you provide examples of machinery or equipment that frequently use brake motors?
In various industrial and manufacturing applications, brake motors are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment. These motors provide braking functionality and enhance the safety and control of rotating machinery. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that frequently utilize brake motors:
- Conveyor Systems: Brake motors are extensively used in conveyor systems, where they control the movement and stopping of conveyor belts. They ensure smooth and controlled starting, stopping, and positioning of material handling conveyors in industries such as logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing.
- Hoists and Cranes: Brake motors are employed in hoists and cranes to provide reliable load holding and controlled lifting operations. They ensure secure stopping and prevent unintended movement of loads during lifting, lowering, or suspension of heavy objects in construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and other settings.
- Elevators and Lifts: Brake motors are an integral part of elevator and lift systems. They facilitate controlled starting, stopping, and leveling of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and other structures.
- Metalworking Machinery: Brake motors are commonly used in metalworking machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. They enable precise control and stopping of rotating spindles, ensuring safe machining operations and preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled rotation.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Brake motors are found in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. They provide controlled stopping and precise positioning of printing cylinders, rollers, or packaging components, ensuring accurate printing, packaging, and labeling processes.
- Textile Machinery: In textile manufacturing, brake motors are used in various machinery, including spinning machines, looms, and winding machines. They enable controlled stopping and tension control of yarns, threads, or fabrics, enhancing safety and quality in textile production.
- Machine Tools: Brake motors are widely employed in machine tools such as grinders, saws, and machining centers. They enable controlled stopping and tool positioning, ensuring precise machining operations and minimizing the risk of tool breakage or workpiece damage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Brake motors are utilized in material handling equipment such as forklifts, pallet trucks, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). They provide controlled stopping and holding capabilities, enhancing the safety and stability of load transport and movement within warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
- Winches and Winders: Brake motors are commonly used in winches and winders for applications such as cable pulling, wire winding, or spooling operations. They ensure controlled stopping, load holding, and precise tension control, contributing to safe and efficient winching or winding processes.
- Industrial Fans and Blowers: Brake motors are employed in industrial fans and blowers used for ventilation, cooling, or air circulation purposes. They provide controlled stopping and prevent the fan or blower from freewheeling when power is turned off, ensuring safe operation and avoiding potential hazards.
These examples represent just a selection of the machinery and equipment where brake motors are frequently utilized. Brake motors are versatile components that enhance safety, control, and performance in numerous industrial applications, ensuring reliable stopping, load holding, and motion control in rotating machinery.
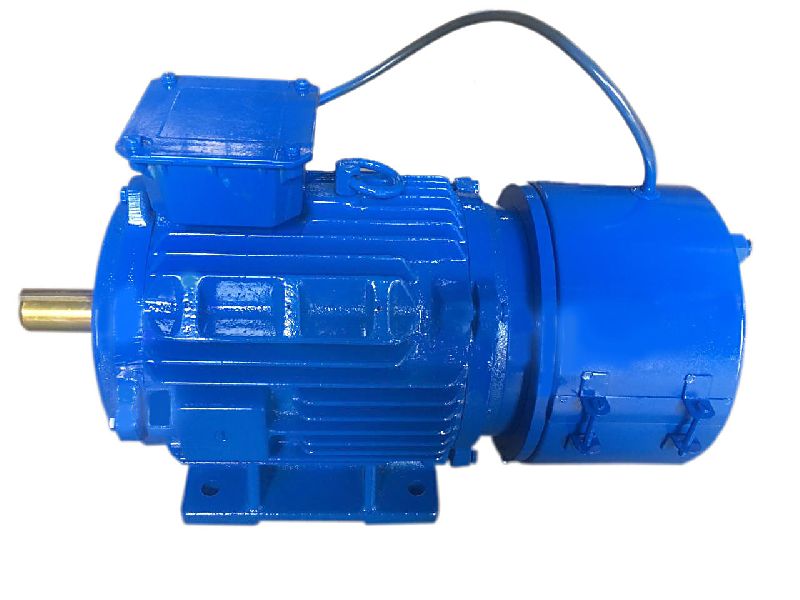

What is a brake motor and how does it operate?
A brake motor is a type of electric motor that incorporates a mechanical braking system. It is designed to provide both motor power and braking functionality in a single unit. The brake motor is commonly used in applications where rapid and precise stopping or holding of loads is required. Here's a detailed explanation of what a brake motor is and how it operates:
A brake motor consists of two main components: the electric motor itself and a braking mechanism. The electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive a load. The braking mechanism, usually located at the non-drive end of the motor, provides the necessary braking force to stop or hold the load when the motor is turned off or power is cut off.
The braking mechanism in a brake motor typically employs one of the following types of brakes:
- Electromagnetic Brake: An electromagnetic brake is the most common type used in brake motors. It consists of an electromagnetic coil and a brake shoe or armature. When the motor is powered, the electromagnetic coil is energized, creating a magnetic field that attracts the brake shoe or armature. This releases the brake and allows the motor to rotate and drive the load. When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the electromagnetic coil is de-energized, and the brake shoe or armature is pressed against a stationary surface, creating friction and stopping the motor's rotation.
- Mechanical Brake: Some brake motors use mechanical brakes, such as disc brakes or drum brakes. These brakes employ friction surfaces, such as brake pads or brake shoes, which are pressed against a rotating disc or drum attached to the motor shaft. When the motor is powered, the brake is disengaged, allowing the motor to rotate. When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, a mechanical mechanism, such as a spring or a cam, engages the brake, creating friction and stopping the motor's rotation.
The operation of a brake motor involves the following steps:
- Motor Operation: When power is supplied to the brake motor, the electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is used to drive the load. The brake is disengaged, allowing the motor shaft to rotate freely.
- Stopping or Holding: When the power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism is engaged. In the case of an electromagnetic brake, the electromagnetic coil is de-energized, and the brake shoe or armature is pressed against a stationary surface, creating friction and stopping the motor's rotation. In the case of a mechanical brake, a mechanical mechanism engages the brake pads or shoes against a rotating disc or drum, creating friction and stopping the motor's rotation.
- Release and Restart: To restart the motor, power is supplied again, and the braking mechanism is disengaged. In the case of an electromagnetic brake, the electromagnetic coil is energized, releasing the brake shoe or armature. In the case of a mechanical brake, the mechanical mechanism disengages the brake pads or shoes from the rotating disc or drum.
Brake motors are commonly used in applications that require precise stopping or holding of loads, such as cranes, hoists, conveyors, machine tools, and elevators. The incorporation of a braking system within the motor eliminates the need for external braking devices or additional components, simplifying the design and installation process. Brake motors enhance safety, efficiency, and control in industrial applications by providing reliable and rapid braking capabilities.


editor by CX 2024-05-17
China OEM Power Electric Wheelchair 250W*2 High-Power Brushless Motor Carbon Fiber Material Intelligent Brake Foldable vacuum pump ac
Product Description
Products Description
Product Paramenters
|
Properties |
Rehabilitation Therapy Supplies |
|
Model Number |
BC-EC8002 |
|
Type |
Electric Wheelchair |
|
Product Name |
Foldable Carbon Fiber Electric Wheelchair |
|
Material |
Carbon Fiber |
|
Remote Control |
Optional |
|
Packing Size |
67*38*79cm |
|
Weight |
17KG |
|
Certificate |
CE ISO13485 ISO9001 |
|
Battery |
24V 12AH Lithium Battery |
|
Motor |
Upgrade aluminum alloy 250W*2 Brushless |
|
Warranty |
24 Months |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Customized: | Customized |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO, RoHS, CE, FDA 510K |
| Condition: | New |
| Tilted: | Tilted |
| Folded: | Folding |
| Leg Rest Type: | Across Both Sides |
| Samples: |
US$ 970/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can brake motors be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Brake motors can indeed be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments, provided they are appropriately designed and protected against the specific conditions they will encounter. The adaptability of brake motors allows them to function effectively and safely in diverse operating environments. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor settings:
- Indoor Adaptation: Brake motors intended for indoor use are typically designed to meet the specific requirements of indoor environments. They are often constructed with enclosures that protect the motor from dust, debris, and moisture commonly found indoors. These enclosures can be in the form of drip-proof (DP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) designs. The enclosures prevent contaminants from entering the motor and ensure reliable and efficient operation in indoor settings.
- Outdoor Adaptation: When brake motors are required for outdoor applications, they need to be adapted to withstand the challenges posed by outdoor conditions, such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to elements. Outdoor-rated brake motors are designed with additional protective measures to ensure their durability and performance. They may feature weatherproof enclosures, such as totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) enclosures with added gaskets and seals to prevent water ingress. These enclosures provide effective protection against rain, snow, dust, and other outdoor elements, allowing the motor to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
- Environmental Sealing: Brake motors can be equipped with environmental seals to further enhance their adaptability for both indoor and outdoor use. These seals provide an additional layer of protection against the entry of moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Depending on the specific application requirements, the seals can be applied to the motor's shaft, housing, or other vulnerable areas to ensure proper sealing and prevent damage or performance degradation due to environmental factors.
- Corrosion Resistance: In certain outdoor environments or specific indoor settings with corrosive elements, brake motors can be designed with corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These specialized materials, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, provide protection against corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt air. Corrosion-resistant brake motors are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance in corrosive environments.
- Temperature Considerations: Brake motors must be adapted to handle the temperature ranges encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. For indoor applications, motors may be designed to operate within a specific temperature range, ensuring reliable performance without overheating. Outdoor-rated brake motors may have additional cooling features, such as oversized cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat effectively and operate within acceptable temperature limits. Heating elements can also be incorporated to prevent condensation and maintain optimal operating temperatures in outdoor or highly humid indoor environments.
- IP Rating: In addition to the specific adaptations mentioned above, brake motors for both indoor and outdoor use are often assigned an Ingress Protection (IP) rating. The IP rating indicates the motor's level of protection against solid particles (first digit) and water ingress (second digit). The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection offered. IP ratings help users select brake motors that are suitable for their intended environment by considering factors such as dust resistance, water resistance, and overall environmental durability.
By incorporating appropriate enclosures, environmental seals, corrosion-resistant materials, temperature management features, and IP ratings, brake motors can be successfully adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments. These adaptations ensure that the motors are well-protected, perform reliably, and maintain their efficiency and longevity, regardless of the operating conditions they are exposed to.

Can you provide examples of machinery or equipment that frequently use brake motors?
In various industrial and manufacturing applications, brake motors are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment. These motors provide braking functionality and enhance the safety and control of rotating machinery. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that frequently utilize brake motors:
- Conveyor Systems: Brake motors are extensively used in conveyor systems, where they control the movement and stopping of conveyor belts. They ensure smooth and controlled starting, stopping, and positioning of material handling conveyors in industries such as logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing.
- Hoists and Cranes: Brake motors are employed in hoists and cranes to provide reliable load holding and controlled lifting operations. They ensure secure stopping and prevent unintended movement of loads during lifting, lowering, or suspension of heavy objects in construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and other settings.
- Elevators and Lifts: Brake motors are an integral part of elevator and lift systems. They facilitate controlled starting, stopping, and leveling of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and other structures.
- Metalworking Machinery: Brake motors are commonly used in metalworking machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. They enable precise control and stopping of rotating spindles, ensuring safe machining operations and preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled rotation.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Brake motors are found in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. They provide controlled stopping and precise positioning of printing cylinders, rollers, or packaging components, ensuring accurate printing, packaging, and labeling processes.
- Textile Machinery: In textile manufacturing, brake motors are used in various machinery, including spinning machines, looms, and winding machines. They enable controlled stopping and tension control of yarns, threads, or fabrics, enhancing safety and quality in textile production.
- Machine Tools: Brake motors are widely employed in machine tools such as grinders, saws, and machining centers. They enable controlled stopping and tool positioning, ensuring precise machining operations and minimizing the risk of tool breakage or workpiece damage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Brake motors are utilized in material handling equipment such as forklifts, pallet trucks, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). They provide controlled stopping and holding capabilities, enhancing the safety and stability of load transport and movement within warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
- Winches and Winders: Brake motors are commonly used in winches and winders for applications such as cable pulling, wire winding, or spooling operations. They ensure controlled stopping, load holding, and precise tension control, contributing to safe and efficient winching or winding processes.
- Industrial Fans and Blowers: Brake motors are employed in industrial fans and blowers used for ventilation, cooling, or air circulation purposes. They provide controlled stopping and prevent the fan or blower from freewheeling when power is turned off, ensuring safe operation and avoiding potential hazards.
These examples represent just a selection of the machinery and equipment where brake motors are frequently utilized. Brake motors are versatile components that enhance safety, control, and performance in numerous industrial applications, ensuring reliable stopping, load holding, and motion control in rotating machinery.

How do brake motors handle variations in load and stopping requirements?
Brake motors are designed to handle variations in load and stopping requirements by incorporating specific features and mechanisms that allow for flexibility and adaptability. These features enable brake motors to effectively respond to changes in load conditions and meet the diverse stopping requirements of different applications. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors handle variations in load and stopping requirements:
1. Adjustable Braking Torque: Brake motors often have adjustable braking torque, allowing operators to modify the stopping force according to the specific load requirements. By adjusting the braking torque, brake motors can accommodate variations in load size, weight, and inertia. Higher braking torque can be set for heavier loads, while lower braking torque can be selected for lighter loads, ensuring optimal stopping performance and preventing excessive wear or damage to the braking system.
2. Controlled Response Time: Brake motors provide controlled response times, allowing for precise and efficient stopping according to the application requirements. The response time refers to the duration between the command to stop and the actual cessation of rotation. Brake motors can be designed with adjustable response times, enabling operators to set the desired stopping speed based on the load characteristics and safety considerations. This flexibility ensures that the braking action is appropriately matched to the load and stopping requirements.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is a feature found in some brake motors that helps handle variations in load and stopping requirements. When the motor is de-energized, dynamic braking converts the kinetic energy of the rotating load into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. This braking mechanism allows brake motors to handle different load conditions and varying stopping requirements, dissipating excess energy and bringing the rotating equipment to a controlled stop.
4. Integrated Control Systems: Brake motors often come equipped with integrated control systems that allow for customized programming and adjustment of the braking parameters. These control systems enable operators to adapt the braking performance based on the load characteristics and stopping requirements. By adjusting parameters such as braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, brake motors can handle variations in load and achieve the desired stopping performance for different applications.
5. Monitoring and Feedback: Some brake motor systems incorporate monitoring and feedback mechanisms to provide real-time information about the load conditions and stopping performance. This feedback can include data on motor temperature, current consumption, or position feedback from encoders or sensors. By continuously monitoring these parameters, brake motors can dynamically adjust their braking action to accommodate variations in load and ensure optimal stopping performance.
6. Adaptable Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with consideration for load variations and stopping requirements. The brake design takes into account factors such as braking surface area, material composition, and cooling methods. These design features allow brake motors to handle different load conditions effectively and provide consistent and reliable stopping performance under varying circumstances.
By incorporating adjustable braking torque, controlled response time, dynamic braking, integrated control systems, monitoring and feedback mechanisms, and adaptable brake designs, brake motors can handle variations in load and stopping requirements. These features enhance the versatility and performance of brake motors, making them suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-10
China supplier Power Electric Wheelchair 250W*2 High-Power Brushless Motor Carbon Fiber Material Intelligent Brake Foldable vacuum pump distributors
Product Description
| Maxium Speed | Weight Capacity | Driving Range | Climbing Range |
| 6km/h | 120kg | 14-24km | 6° |
| Dimensions | Charging Time | Motor | Battery |
| 972x623x725mm | 3-6H | 150W*2 | Lithium 24V6AH((10AH/12AH option) |
More products
Quality Management System
Profession team with R&D, Quality Inspection, Quality Control, Quality Assurance, Production Management, Tracking System. Certified by EN12184, ISO9001, ISO13485, EMC ,FDA and in according with compliance standard.
Company Profile
HangZhou Sweetrich vehicle industry technology Co.,LTD was settled on HangZhou Industrial Zone, ZheJiang in 2011, which is a high-tech company covering an area of 60 acres with 30,000 square CHINAMFG of factory. And we have accumulated eleven-year experience of R&D and production of mobility scooter and power wheelchair. Focusing on the well-being and convenience of the elderly and handicapped people and always dedicating to enable vulnerable groups to be more independent, more dignified.
Sweetrich possesses the intellectual property right of our electric scooters and power wheelchairs. The products are user friendly designed to ensure users' comfort. They also have international advanced control technology and driving system to secure the smooth and safe drive. We design the carriage body scientifically and manage our production process strictly to guarantee the reliability of our functional products.
After many years development experience we have reached and got high reputation from our customers. Many customers have become our long-term business partners!
"Quality first, credit above and customer supreme " is our permanent operating objective. We believe that the market is a true test of the vitality of enterprises.
Facing the fierce market competition, Sweetrich ensures the promise to customers by qualified products, considerable service and reasonable price. Sweetrich has been exported to America,Europe,Japan,Australian,middle-east and so on.
We are looking CHINAMFG to establishing long term cooperation with you!
Testing Facilities
Company History
Exhibition
FAQ
Q1: Are you a manufacturer or trading company?
A1: We have our own factory to produce this products, and warmly welcome to visit us
at your convenient.
Q2: What about the shipping methods?
A2: By express/By air/By sea.
Q3: What about the payment methods?
A3: We accept T/T, L/C for big amount, and for small amount, you can pay us by Paypal,Western Union, Moneygram, Escrow etc.
04:What's your delivery lime?
A4: Usually we produce within 35 working days after receiving the payment.
Q5: Can I print our logo on your products?
A5: Yes, of course,we can do as your own design, just with small quantity, you need to pay film cost.
Q6: Can I order some samples for our testing?
A6: Sure, We will refund back you sample cost from the official order directly.
Q7: What's your MOQ( Minimum Order Quantity ) of each products?
A7: NO MOQ but price is different for different quantity.
Q8: OEM and ODM is available?
A8: Yes, we do OEM and ODM.
Q9: What is the product warranty?
A8: 1 year for the frame, and we will provide the wearing parts for replacement within 2
years freely.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Customized: | Customized |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO, RoHS, CE |
| Condition: | New |
| Tilted: | Non-Tilted |
| Folded: | Folding |
| Leg Rest Type: | Both Sides Separate |
| Samples: |
US$ 900/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can brake motors be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Brake motors can indeed be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments, provided they are appropriately designed and protected against the specific conditions they will encounter. The adaptability of brake motors allows them to function effectively and safely in diverse operating environments. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor settings:
- Indoor Adaptation: Brake motors intended for indoor use are typically designed to meet the specific requirements of indoor environments. They are often constructed with enclosures that protect the motor from dust, debris, and moisture commonly found indoors. These enclosures can be in the form of drip-proof (DP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) designs. The enclosures prevent contaminants from entering the motor and ensure reliable and efficient operation in indoor settings.
- Outdoor Adaptation: When brake motors are required for outdoor applications, they need to be adapted to withstand the challenges posed by outdoor conditions, such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to elements. Outdoor-rated brake motors are designed with additional protective measures to ensure their durability and performance. They may feature weatherproof enclosures, such as totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) enclosures with added gaskets and seals to prevent water ingress. These enclosures provide effective protection against rain, snow, dust, and other outdoor elements, allowing the motor to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
- Environmental Sealing: Brake motors can be equipped with environmental seals to further enhance their adaptability for both indoor and outdoor use. These seals provide an additional layer of protection against the entry of moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Depending on the specific application requirements, the seals can be applied to the motor's shaft, housing, or other vulnerable areas to ensure proper sealing and prevent damage or performance degradation due to environmental factors.
- Corrosion Resistance: In certain outdoor environments or specific indoor settings with corrosive elements, brake motors can be designed with corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These specialized materials, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, provide protection against corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt air. Corrosion-resistant brake motors are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance in corrosive environments.
- Temperature Considerations: Brake motors must be adapted to handle the temperature ranges encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. For indoor applications, motors may be designed to operate within a specific temperature range, ensuring reliable performance without overheating. Outdoor-rated brake motors may have additional cooling features, such as oversized cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat effectively and operate within acceptable temperature limits. Heating elements can also be incorporated to prevent condensation and maintain optimal operating temperatures in outdoor or highly humid indoor environments.
- IP Rating: In addition to the specific adaptations mentioned above, brake motors for both indoor and outdoor use are often assigned an Ingress Protection (IP) rating. The IP rating indicates the motor's level of protection against solid particles (first digit) and water ingress (second digit). The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection offered. IP ratings help users select brake motors that are suitable for their intended environment by considering factors such as dust resistance, water resistance, and overall environmental durability.
By incorporating appropriate enclosures, environmental seals, corrosion-resistant materials, temperature management features, and IP ratings, brake motors can be successfully adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments. These adaptations ensure that the motors are well-protected, perform reliably, and maintain their efficiency and longevity, regardless of the operating conditions they are exposed to.

How do manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors?
Manufacturers employ various processes and measures to ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors. These processes involve rigorous testing, adherence to industry standards, quality control procedures, and continuous improvement initiatives. Here's a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors:
- Design and Engineering: Manufacturers invest considerable effort in the design and engineering phase of brake motors. They employ experienced engineers and designers who follow industry best practices and utilize advanced design tools to develop motors with robust and reliable braking systems. Thorough analysis, simulations, and prototyping are conducted to optimize the motor's performance, efficiency, and safety features.
- Material Selection: High-quality materials are chosen for the construction of brake motors. Manufacturers carefully select components such as motor windings, brake discs, brake pads, and housing materials to ensure durability, heat resistance, and optimal friction characteristics. The use of quality materials enhances the motor's reliability and contributes to its long-term performance.
- Manufacturing Processes: Stringent manufacturing processes are implemented to ensure consistent quality and reliability. Manufacturers employ advanced machinery and automation techniques for precision assembly and production. Strict quality control measures are applied at each stage of manufacturing to detect and rectify any defects or deviations from specifications.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Brake motors undergo comprehensive testing and quality assurance procedures before they are released to the market. These tests include performance testing, load testing, endurance testing, and environmental testing. Manufacturers verify that the motors meet or exceed industry standards and performance specifications. Additionally, they conduct safety tests to ensure compliance with applicable safety regulations and standards.
- Certifications and Compliance: Manufacturers seek certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations. This may include certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or certifications specific to the motor industry, such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. Compliance with these standards demonstrates the manufacturer's commitment to producing high-quality and reliable brake motors.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Manufacturers implement robust quality control processes throughout the production cycle. This includes inspection of raw materials, in-process inspections during manufacturing, and final inspections before shipment. Quality control personnel conduct visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance evaluations to ensure that each brake motor meets the specified quality criteria.
- Continuous Improvement: Manufacturers prioritize continuous improvement initiatives to enhance the quality and reliability of brake motors. They actively seek customer feedback, monitor field performance, and conduct post-production evaluations to identify areas for improvement. This feedback loop helps manufacturers refine their designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control procedures, leading to increased reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Support and Warranty: Manufacturers provide comprehensive customer support and warranty programs for their brake motors. They offer technical assistance, troubleshooting guides, and maintenance recommendations to customers. Warranty coverage ensures that any manufacturing defects or malfunctions are addressed promptly, bolstering customer confidence in the quality and reliability of the brake motors.
By employing robust design and engineering processes, meticulous material selection, stringent manufacturing processes, comprehensive testing and quality assurance procedures, certifications and compliance with industry standards, rigorous quality control and inspection measures, continuous improvement initiatives, and dedicated customer support and warranty programs, manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors. These measures contribute to the production of high-performance motors that meet the safety, durability, and performance requirements of industrial and manufacturing applications.

How do brake motors handle variations in load and stopping requirements?
Brake motors are designed to handle variations in load and stopping requirements by incorporating specific features and mechanisms that allow for flexibility and adaptability. These features enable brake motors to effectively respond to changes in load conditions and meet the diverse stopping requirements of different applications. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors handle variations in load and stopping requirements:
1. Adjustable Braking Torque: Brake motors often have adjustable braking torque, allowing operators to modify the stopping force according to the specific load requirements. By adjusting the braking torque, brake motors can accommodate variations in load size, weight, and inertia. Higher braking torque can be set for heavier loads, while lower braking torque can be selected for lighter loads, ensuring optimal stopping performance and preventing excessive wear or damage to the braking system.
2. Controlled Response Time: Brake motors provide controlled response times, allowing for precise and efficient stopping according to the application requirements. The response time refers to the duration between the command to stop and the actual cessation of rotation. Brake motors can be designed with adjustable response times, enabling operators to set the desired stopping speed based on the load characteristics and safety considerations. This flexibility ensures that the braking action is appropriately matched to the load and stopping requirements.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is a feature found in some brake motors that helps handle variations in load and stopping requirements. When the motor is de-energized, dynamic braking converts the kinetic energy of the rotating load into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. This braking mechanism allows brake motors to handle different load conditions and varying stopping requirements, dissipating excess energy and bringing the rotating equipment to a controlled stop.
4. Integrated Control Systems: Brake motors often come equipped with integrated control systems that allow for customized programming and adjustment of the braking parameters. These control systems enable operators to adapt the braking performance based on the load characteristics and stopping requirements. By adjusting parameters such as braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, brake motors can handle variations in load and achieve the desired stopping performance for different applications.
5. Monitoring and Feedback: Some brake motor systems incorporate monitoring and feedback mechanisms to provide real-time information about the load conditions and stopping performance. This feedback can include data on motor temperature, current consumption, or position feedback from encoders or sensors. By continuously monitoring these parameters, brake motors can dynamically adjust their braking action to accommodate variations in load and ensure optimal stopping performance.
6. Adaptable Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with consideration for load variations and stopping requirements. The brake design takes into account factors such as braking surface area, material composition, and cooling methods. These design features allow brake motors to handle different load conditions effectively and provide consistent and reliable stopping performance under varying circumstances.
By incorporating adjustable braking torque, controlled response time, dynamic braking, integrated control systems, monitoring and feedback mechanisms, and adaptable brake designs, brake motors can handle variations in load and stopping requirements. These features enhance the versatility and performance of brake motors, making them suitable for a wide range of applications across different industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-08
China High Power Electric Car Brushless DC Planetary Gear Servo BLDC Motor for DIY CNC Mill motor electric
Solution Description
| 36BL DC Brushless Motor | |||||
| Basic Information | |||||
| Item | Performance | ||||
| Tem. Rise | 50K max | ||||
| Humidity | 65% | ||||
| Working Tem. | (-30ºC~+85ºC) | ||||
| Insulation Resistance | 100MΩ min 250VDC | ||||
| Surge Take a look at | 350VAC for 3s | ||||
| Insulation Course | A | ||||
| Drive Method | Three period total wave PWM modulation | ||||
| Motor Spec. | |||||||||
| PN | Rated Voltage | Noload Velocity | Noload Recent | Rated Load | Load Velocity | Load Present | Power | Stall Present | Section |
| VDC | rpm±10% | mA±10% | mN.m | rpm±10% | mA±10% | W | A | ||
| 36BLDC-002 | 24 | 6700 | 100 | 19.one | 5000 | 680 | ten | two.5 | 3 |
Probond motors styles brush, brushless, stepper, hysteresis and linear motors to fulfill clients specifications.
Our motors use common and specific parts with buyer picked torque/velocity requirements that can be modified to your applications.
The AC/DC equipment motors are based on to unique magetic circuits that improve motor layout for high velocity low torque and reduced pace higher torque.
These motors give you decrease rotational losses, excellent thermal transfer, interchangeable conclude caps, effortlessly sealed. Possibilities incorporate connectors, encoders, shaft modifications, dimensional changes, etc.
Probond motor owns professional revenue staff and engineer staff with more than 10 a long time expertise in motor industry, based on China mainland dealing with overseas business for a long time, we know your wants greater than others.
Probond Sonicare Toothbrush Motor and Thermostatic Valve Hysteresis Motor are our very hot items on sell in 2017 with extremely good quality stage and competitive price tag.
Remember to kindly speak to us to get a catalogue.
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| 36BL DC Brushless Motor | |||||
| Basic Information | |||||
| Item | Performance | ||||
| Tem. Rise | 50K max | ||||
| Humidity | 65% | ||||
| Working Tem. | (-30ºC~+85ºC) | ||||
| Insulation Resistance | 100MΩ min 250VDC | ||||
| Surge Test | 350VAC for 3s | ||||
| Insulation Class | A | ||||
| Drive Mode | Three phase full wave PWM modulation | ||||
###
| Motor Spec. | |||||||||
| PN | Rated Voltage | Noload Speed | Noload Current | Rated Load | Load Speed | Load Current | Power | Stall Current | Phase |
| VDC | rpm±10% | mA±10% | mN.m | rpm±10% | mA±10% | W | A | ||
| 36BLDC-002 | 24 | 6700 | 100 | 19.1 | 5000 | 680 | 10 | 2.5 | 3 |
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Adjust Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Excited |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| 36BL DC Brushless Motor | |||||
| Basic Information | |||||
| Item | Performance | ||||
| Tem. Rise | 50K max | ||||
| Humidity | 65% | ||||
| Working Tem. | (-30ºC~+85ºC) | ||||
| Insulation Resistance | 100MΩ min 250VDC | ||||
| Surge Test | 350VAC for 3s | ||||
| Insulation Class | A | ||||
| Drive Mode | Three phase full wave PWM modulation | ||||
###
| Motor Spec. | |||||||||
| PN | Rated Voltage | Noload Speed | Noload Current | Rated Load | Load Speed | Load Current | Power | Stall Current | Phase |
| VDC | rpm±10% | mA±10% | mN.m | rpm±10% | mA±10% | W | A | ||
| 36BLDC-002 | 24 | 6700 | 100 | 19.1 | 5000 | 680 | 10 | 2.5 | 3 |
The Basics of a Planetary Motor
A Planetary Motor is a type of gearmotor that uses multiple planetary gears to deliver torque. This system minimizes the chances of failure of individual gears and increases output capacity. Compared to the planetary motor, the spur gear motor is less complex and less expensive. However, a spur gear motor is generally more suitable for applications requiring low torque. This is because each gear is responsible for the entire load, limiting its torque.
Self-centering planetary gears
This self-centering mechanism for a planetary motor is based on a helical arrangement. The helical structure involves a sun-planet, with its crown and slope modified. The gears are mounted on a ring and share the load evenly. The helical arrangement can be either self-centering or self-resonant. This method is suited for both applications.
A helical planetary gear transmission is illustrated in FIG. 1. A helical configuration includes an output shaft 18 and a sun gear 18. The drive shaft extends through an opening in the cover to engage drive pins on the planet carriers. The drive shaft of the planetary gears can be fixed to the helical arrangement or can be removable. The transmission system is symmetrical, allowing the output shaft of the planetary motor to rotate radially in response to the forces acting on the planet gears.
A flexible pin can improve load sharing. This modification may decrease the face load distribution, but increases the (K_Hbeta) parameter. This effect affects the gear rating and life. It is important to understand the effects of flexible pins. It is worth noting that there are several other disadvantages of flexible pins in helical PGSs. The benefits of flexible pins are discussed below.
Using self-centering planetary gears for a helical planetary motor is essential for symmetrical force distribution. These gears ensure the symmetry of force distribution. They can also be used for self-centering applications. Self-centering planetary gears also guarantee the proper force distribution. They are used to drive a planetary motor. The gearhead is made of a ring gear, and the output shaft is supported by two ball bearings. Self-centering planetary gears can handle a high torque input, and can be suited for many applications.
To solve for a planetary gear mechanism, you need to find its pitch curve. The first step is to find the radius of the internal gear ring. A noncircular planetary gear mechanism should be able to satisfy constraints that can be complex and nonlinear. Using a computer, you can solve for these constraints by analyzing the profile of the planetary wheel's tooth curve.
High torque
Compared to the conventional planetary motors, high-torque planetary motors have a higher output torque and better transmission efficiency. The high-torque planetary motors are designed to withstand large loads and are used in many types of applications, such as medical equipment and miniature consumer electronics. Their compact design makes them suitable for small space-saving applications. In addition, these motors are designed for high-speed operation.
They come with a variety of shaft configurations and have a wide range of price-performance ratios. The FAULHABER planetary gearboxes are made of plastic, resulting in a good price-performance ratio. In addition, plastic input stage gears are used in applications requiring high torques, and steel input stage gears are available for higher speeds. For difficult operating conditions, modified lubrication is available.
Various planetary gear motors are available in different sizes and power levels. Generally, planetary gear motors are made of steel, brass, or plastic, though some use plastic for their gears. Steel-cut gears are the most durable, and are ideal for applications that require a high amount of torque. Similarly, nickel-steel gears are more lubricated and can withstand a high amount of wear.
The output torque of a high-torque planetary gearbox depends on its rated input speed. Industrial-grade high-torque planetary gearboxes are capable of up to 18000 RPM. Their output torque is not higher than 2000 nm. They are also used in machines where a planet is decelerating. Their working temperature ranges between 25 and 100 degrees Celsius. For best results, it is best to choose the right size for the application.
A high-torque planetary gearbox is the most suitable type of high-torque planetary motor. It is important to determine the deceleration ratio before buying one. If there is no product catalog that matches your servo motor, consider buying a close-fitting high-torque planetary gearbox. There are also high-torque planetary gearboxes available for custom-made applications.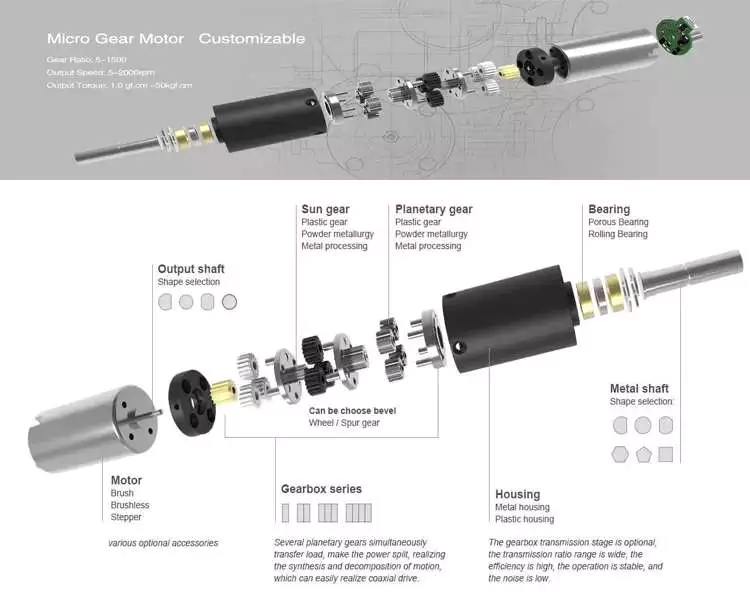
High efficiency
A planetary gearbox is a type of mechanical device that is used for high-torque transmission. This gearbox is made of multiple pairs of gears. Large gears on the output shaft mesh with small gears on the input shaft. The ratio between the big and small gear teeth determines the transmittable torque. High-efficiency planetary gearheads are available for linear motion, axial loads, and sterilizable applications.
The AG2400 high-end gear unit series is ideally matched to Beckhoff's extensive line of servomotors and gearboxes. Its single-stage and multi-stage transmission ratios are highly flexible and can be matched to different robot types. Its modified lubrication helps it operate in difficult operating conditions. These high-performance gear units are available in a wide range of sizes.
A planetary gear motor can be made of steel, nickel-steel, or brass. In addition to steel, some models use plastic. The planetary gears share work between multiple gears, making it easy to transfer high amounts of power without putting a lot of stress on the gears. The gears in a planetary gear motor are held together by a movable arm. High-efficiency planetary gear motors are more efficient than traditional gearmotors.
While a planetary gear motor can generate torque, it is more efficient and cheaper to produce. The planetary gear system is designed with all gears operating in synchrony, minimizing the chance of a single gear failure. The efficiency of a planetary gearmotor makes it a popular choice for high-torque applications. This type of motor is suitable for many applications, and is less expensive than a standard geared motor.
The planetary gearbox is a combination of a planetary type gearbox and a DC motor. The planetary gearbox is compact, versatile, and efficient, and can be used in a wide range of industrial environments. The planetary gearbox with an HN210 DC motor is used in a 22mm OD, PPH, and ph configuration with voltage operating between 6V and 24V. It is available in many configurations and can be custom-made to meet your application requirements.
High cost
In general, planetary gearmotors are more expensive than other configurations of gearmotors. This is due to the complexity of their design, which involves the use of a central sun gear and a set of planetary gears which mesh with each other. The entire assembly is enclosed in a larger internal tooth gear. However, planetary motors are more effective for higher load requirements. The cost of planetary motors varies depending on the number of gears and the number of planetary gears in the system.
If you want to build a planetary gearbox, you can purchase a gearbox for the motor. These gearboxes are often available with several ratios, and you can use any one to create a custom ratio. The cost of a gearbox depends on how much power you want to move with the gearbox, and how much gear ratio you need. You can even contact your local FRC team to purchase a gearbox for the motor.
Gearboxes play a major role in determining the efficiency of a planetary gearmotor. The output shafts used for this type of motor are usually made of steel or nickel-steel, while those used in planetary gearboxes are made from brass or plastic. The former is the most durable and is best for applications that require high torque. The latter, however, is more absorbent and is better at holding lubricant.
Using a planetary gearbox will allow you to reduce the input power required for the stepper motor. However, this is not without its downsides. A planetary gearbox can also be replaced with a spare part. A planetary gearbox is inexpensive, and its spare parts are inexpensive. A planetary gearbox has low cost compared to a planetary motor. Its advantages make it more desirable in certain applications.
Another advantage of a planetary gear unit is the ability to handle ultra-low speeds. Using a planetary gearbox allows stepper motors to avoid resonance zones, which can cause them to crawl. In addition, the planetary gear unit allows for safe and efficient cleaning. So, whether you're considering a planetary gear unit for a particular application, these gear units can help you get exactly what you need.


editor by czh 2022-12-17
China High Power Permanent Magnet Tattoo Coreless Planetary Gear/Reduction/Deceleration/Gearbox Brushless BLDC Electric Micro Mini DC Motor wholesaler
Product Description
Quiet stable and reliable for long life operation
1.Diameters: 57mm
2.Lengths: 56mm;76mm;96mm
3.Continuous torques: 0.11Nm;0.22Nm;0.32Nm
4.Power: 46W;92W;134W
5.Speeds up to 4000rpm;4000rpm;4000rpm
6.Environmental conditions: -10~+40°C
7.Number of poles/phase:4/3
8.Mangnet material:Bonded NdFeB
9.Insulation class:B
10.Optional: electronic drivers, encoders and gearheads, as well as Hall effect resolver and sensorless feedback
11.We can design the special voltage and shaft and so on
|
US $15-40 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools, Medical Equpiments |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Compound |
| Function: | Driving |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brush |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
|
US $15-40 / Piece | |
100 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Car, Power Tools, Medical Equpiments |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Compound |
| Function: | Driving |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brush |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 20/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
The Basics of a Planetary Motor
A Planetary Motor is a type of gearmotor that uses multiple planetary gears to deliver torque. This system minimizes the chances of failure of individual gears and increases output capacity. Compared to the planetary motor, the spur gear motor is less complex and less expensive. However, a spur gear motor is generally more suitable for applications requiring low torque. This is because each gear is responsible for the entire load, limiting its torque.
Self-centering planetary gears
This self-centering mechanism for a planetary motor is based on a helical arrangement. The helical structure involves a sun-planet, with its crown and slope modified. The gears are mounted on a ring and share the load evenly. The helical arrangement can be either self-centering or self-resonant. This method is suited for both applications.
A helical planetary gear transmission is illustrated in FIG. 1. A helical configuration includes an output shaft 18 and a sun gear 18. The drive shaft extends through an opening in the cover to engage drive pins on the planet carriers. The drive shaft of the planetary gears can be fixed to the helical arrangement or can be removable. The transmission system is symmetrical, allowing the output shaft of the planetary motor to rotate radially in response to the forces acting on the planet gears.
A flexible pin can improve load sharing. This modification may decrease the face load distribution, but increases the (K_Hbeta) parameter. This effect affects the gear rating and life. It is important to understand the effects of flexible pins. It is worth noting that there are several other disadvantages of flexible pins in helical PGSs. The benefits of flexible pins are discussed below.
Using self-centering planetary gears for a helical planetary motor is essential for symmetrical force distribution. These gears ensure the symmetry of force distribution. They can also be used for self-centering applications. Self-centering planetary gears also guarantee the proper force distribution. They are used to drive a planetary motor. The gearhead is made of a ring gear, and the output shaft is supported by two ball bearings. Self-centering planetary gears can handle a high torque input, and can be suited for many applications.
To solve for a planetary gear mechanism, you need to find its pitch curve. The first step is to find the radius of the internal gear ring. A noncircular planetary gear mechanism should be able to satisfy constraints that can be complex and nonlinear. Using a computer, you can solve for these constraints by analyzing the profile of the planetary wheel's tooth curve.
High torque
Compared to the conventional planetary motors, high-torque planetary motors have a higher output torque and better transmission efficiency. The high-torque planetary motors are designed to withstand large loads and are used in many types of applications, such as medical equipment and miniature consumer electronics. Their compact design makes them suitable for small space-saving applications. In addition, these motors are designed for high-speed operation.
They come with a variety of shaft configurations and have a wide range of price-performance ratios. The FAULHABER planetary gearboxes are made of plastic, resulting in a good price-performance ratio. In addition, plastic input stage gears are used in applications requiring high torques, and steel input stage gears are available for higher speeds. For difficult operating conditions, modified lubrication is available.
Various planetary gear motors are available in different sizes and power levels. Generally, planetary gear motors are made of steel, brass, or plastic, though some use plastic for their gears. Steel-cut gears are the most durable, and are ideal for applications that require a high amount of torque. Similarly, nickel-steel gears are more lubricated and can withstand a high amount of wear.
The output torque of a high-torque planetary gearbox depends on its rated input speed. Industrial-grade high-torque planetary gearboxes are capable of up to 18000 RPM. Their output torque is not higher than 2000 nm. They are also used in machines where a planet is decelerating. Their working temperature ranges between 25 and 100 degrees Celsius. For best results, it is best to choose the right size for the application.
A high-torque planetary gearbox is the most suitable type of high-torque planetary motor. It is important to determine the deceleration ratio before buying one. If there is no product catalog that matches your servo motor, consider buying a close-fitting high-torque planetary gearbox. There are also high-torque planetary gearboxes available for custom-made applications.
High efficiency
A planetary gearbox is a type of mechanical device that is used for high-torque transmission. This gearbox is made of multiple pairs of gears. Large gears on the output shaft mesh with small gears on the input shaft. The ratio between the big and small gear teeth determines the transmittable torque. High-efficiency planetary gearheads are available for linear motion, axial loads, and sterilizable applications.
The AG2400 high-end gear unit series is ideally matched to Beckhoff's extensive line of servomotors and gearboxes. Its single-stage and multi-stage transmission ratios are highly flexible and can be matched to different robot types. Its modified lubrication helps it operate in difficult operating conditions. These high-performance gear units are available in a wide range of sizes.
A planetary gear motor can be made of steel, nickel-steel, or brass. In addition to steel, some models use plastic. The planetary gears share work between multiple gears, making it easy to transfer high amounts of power without putting a lot of stress on the gears. The gears in a planetary gear motor are held together by a movable arm. High-efficiency planetary gear motors are more efficient than traditional gearmotors.
While a planetary gear motor can generate torque, it is more efficient and cheaper to produce. The planetary gear system is designed with all gears operating in synchrony, minimizing the chance of a single gear failure. The efficiency of a planetary gearmotor makes it a popular choice for high-torque applications. This type of motor is suitable for many applications, and is less expensive than a standard geared motor.
The planetary gearbox is a combination of a planetary type gearbox and a DC motor. The planetary gearbox is compact, versatile, and efficient, and can be used in a wide range of industrial environments. The planetary gearbox with an HN210 DC motor is used in a 22mm OD, PPH, and ph configuration with voltage operating between 6V and 24V. It is available in many configurations and can be custom-made to meet your application requirements.
High cost
In general, planetary gearmotors are more expensive than other configurations of gearmotors. This is due to the complexity of their design, which involves the use of a central sun gear and a set of planetary gears which mesh with each other. The entire assembly is enclosed in a larger internal tooth gear. However, planetary motors are more effective for higher load requirements. The cost of planetary motors varies depending on the number of gears and the number of planetary gears in the system.
If you want to build a planetary gearbox, you can purchase a gearbox for the motor. These gearboxes are often available with several ratios, and you can use any one to create a custom ratio. The cost of a gearbox depends on how much power you want to move with the gearbox, and how much gear ratio you need. You can even contact your local FRC team to purchase a gearbox for the motor.
Gearboxes play a major role in determining the efficiency of a planetary gearmotor. The output shafts used for this type of motor are usually made of steel or nickel-steel, while those used in planetary gearboxes are made from brass or plastic. The former is the most durable and is best for applications that require high torque. The latter, however, is more absorbent and is better at holding lubricant.
Using a planetary gearbox will allow you to reduce the input power required for the stepper motor. However, this is not without its downsides. A planetary gearbox can also be replaced with a spare part. A planetary gearbox is inexpensive, and its spare parts are inexpensive. A planetary gearbox has low cost compared to a planetary motor. Its advantages make it more desirable in certain applications.
Another advantage of a planetary gear unit is the ability to handle ultra-low speeds. Using a planetary gearbox allows stepper motors to avoid resonance zones, which can cause them to crawl. In addition, the planetary gear unit allows for safe and efficient cleaning. So, whether you're considering a planetary gear unit for a particular application, these gear units can help you get exactly what you need.


editor by czh 2022-11-30