Product Description
Specifications
1) Dimensions of device: 42mm, 60mm, 70mm, 80mm, 90mm, 104mm
2) Power: 6W, 15W, 25W, 40W, 60W, 90W, 120W, 140W
3) Voltage Poles: Single-Phase 100V 50/60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 2P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 2P
Single-Phase 110V,120V 60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 220V,120V 60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 200/220/230V 50/60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 380/415V 50/60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 200/220/230V 50/60Hz 2P
Three-Phase 380/415V 50/60Hz 2P
4) Gear ratio of the Gear Head: 3, 3.6, 5, 6, 7.5, 9, 12.5, 15, 18, 25, 30, 36, 50, 60,75,90,100,120,150,180,250
We are specialized in Mini AC Gear Motor. Our main products are used for MachineTools, Textile Machinery, Medical Appliance, Conveying Machine, Printing Mechanism, Food Machinery, Vending Machine, Packing Machinery, Gumming Machine and so on. We offer customers with top quality products and fine service. Please contact us if you have any question or inquiry.
Our reduction geared motor Advantage
1,reasonable price with excellent quality
2,delivery in time
3,safe ,reliable ,economical and durable
4,stable transmission ,quiet operation
5,smooth running and low noise
6,nice appearance ,durable service life
7,high heat-radiating efficiency ,high carrying ability
8,each gearbox must be tested before packing
9.reply in high efficiency during 1 working day
10. professional to produce gearbox and electric motor .
FAQ
1, Q:what\'s your MOQ for ac gearbox motor ?
A: 1pc is ok for each type electric gear box motor
2, Q: What about your warranty for your induction speed reducer motor ?
A: 1 year ,but except man-made destroyed
3, Q: which payment way you can accept ?
A: TT, western union .
4, Q: how about your payment way ?
A: 100%payment in advanced less $5000 ,30% payment in advanced payment , 70% payment before sending over $5000.
5, Q: how about your packing of speed reduction motor ?
A: plywood case ,if size is small ,we will pack with pallet for less 1 container
6, Q: What information should be given, if I buy electric helical geared motor from you ?
A: rated power, ratio or output speed,type ,voltage , mounting way , quantity , if more is better ,
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can brake motors be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Brake motors can indeed be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments, provided they are appropriately designed and protected against the specific conditions they will encounter. The adaptability of brake motors allows them to function effectively and safely in diverse operating environments. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor settings:
- Indoor Adaptation: Brake motors intended for indoor use are typically designed to meet the specific requirements of indoor environments. They are often constructed with enclosures that protect the motor from dust, debris, and moisture commonly found indoors. These enclosures can be in the form of drip-proof (DP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) designs. The enclosures prevent contaminants from entering the motor and ensure reliable and efficient operation in indoor settings.
- Outdoor Adaptation: When brake motors are required for outdoor applications, they need to be adapted to withstand the challenges posed by outdoor conditions, such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to elements. Outdoor-rated brake motors are designed with additional protective measures to ensure their durability and performance. They may feature weatherproof enclosures, such as totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) enclosures with added gaskets and seals to prevent water ingress. These enclosures provide effective protection against rain, snow, dust, and other outdoor elements, allowing the motor to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
- Environmental Sealing: Brake motors can be equipped with environmental seals to further enhance their adaptability for both indoor and outdoor use. These seals provide an additional layer of protection against the entry of moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Depending on the specific application requirements, the seals can be applied to the motor's shaft, housing, or other vulnerable areas to ensure proper sealing and prevent damage or performance degradation due to environmental factors.
- Corrosion Resistance: In certain outdoor environments or specific indoor settings with corrosive elements, brake motors can be designed with corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These specialized materials, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, provide protection against corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt air. Corrosion-resistant brake motors are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance in corrosive environments.
- Temperature Considerations: Brake motors must be adapted to handle the temperature ranges encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. For indoor applications, motors may be designed to operate within a specific temperature range, ensuring reliable performance without overheating. Outdoor-rated brake motors may have additional cooling features, such as oversized cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat effectively and operate within acceptable temperature limits. Heating elements can also be incorporated to prevent condensation and maintain optimal operating temperatures in outdoor or highly humid indoor environments.
- IP Rating: In addition to the specific adaptations mentioned above, brake motors for both indoor and outdoor use are often assigned an Ingress Protection (IP) rating. The IP rating indicates the motor's level of protection against solid particles (first digit) and water ingress (second digit). The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection offered. IP ratings help users select brake motors that are suitable for their intended environment by considering factors such as dust resistance, water resistance, and overall environmental durability.
By incorporating appropriate enclosures, environmental seals, corrosion-resistant materials, temperature management features, and IP ratings, brake motors can be successfully adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments. These adaptations ensure that the motors are well-protected, perform reliably, and maintain their efficiency and longevity, regardless of the operating conditions they are exposed to.

What maintenance practices are essential for extending the lifespan of a brake motor?
Maintaining a brake motor properly is crucial for extending its lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance practices help prevent premature wear, identify potential issues, and address them promptly. Here are some essential maintenance practices for extending the lifespan of a brake motor:
- Cleanliness: Keeping the brake motor clean is important to prevent the accumulation of dirt, dust, or debris that can affect its performance. Regularly inspect the motor and clean it using appropriate cleaning methods and materials, ensuring that the power is disconnected before performing any cleaning tasks.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the brake motor's moving parts is essential to minimize friction and reduce wear and tear. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the type of lubricant to use and the frequency of lubrication. Ensure that the lubrication points are accessible and apply the lubricant in the recommended amounts.
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections of the brake motor are necessary to identify any signs of damage, loose connections, or abnormal wear. Check for any loose or damaged components, such as bolts, cables, or connectors. Inspect the brake pads or discs for wear and ensure they are properly aligned. If any issues are detected, take appropriate action to address them promptly.
- Brake Adjustment: Periodically check and adjust the brake mechanism of the motor to ensure it maintains proper braking performance. This may involve adjusting the brake pads, ensuring proper clearance, and verifying that the braking force is sufficient. Improper brake adjustment can lead to excessive wear, reduced stopping power, or safety hazards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring the operating temperature of the brake motor is important to prevent overheating and thermal damage. Ensure that the motor is not subjected to excessive ambient temperatures or overloaded conditions. If the motor becomes excessively hot, investigate the cause and take corrective measures, such as improving ventilation or reducing the load.
- Vibration Analysis: Periodic vibration analysis can help detect early signs of mechanical problems or misalignment in the brake motor. Using specialized equipment or vibration monitoring systems, measure and analyze the motor's vibration levels. If abnormal vibrations are detected, investigate and address the underlying issues to prevent further damage.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the electrical connections of the brake motor to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or faulty connections can lead to power issues, motor malfunctions, or electrical hazards. Tighten any loose connections and clean any corrosion using appropriate methods and materials.
- Testing and Calibration: Perform periodic testing and calibration of the brake motor to verify its performance and ensure it operates within the specified parameters. This may involve conducting load tests, verifying braking force, or checking the motor's speed and torque. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines or consult with qualified technicians for proper testing and calibration procedures.
- Documentation and Record-keeping: Maintain a record of all maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and any relevant information related to the brake motor. This documentation helps track the maintenance history, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks effectively. It also serves as a reference for warranty claims or troubleshooting purposes.
- Professional Servicing: In addition to regular maintenance tasks, consider scheduling professional servicing and inspections by qualified technicians. They can perform comprehensive checks, identify potential issues, and perform specialized maintenance procedures that require expertise or specialized tools. Professional servicing can help ensure thorough maintenance and maximize the lifespan of the brake motor.
By following these essential maintenance practices, brake motor owners can enhance the lifespan of the motor, reduce the risk of unexpected failures, and maintain its optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only extends the motor's lifespan but also contributes to safe operation, energy efficiency, and overall reliability.

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here's a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China factory 60# 220V 400W AC Permanent Magnet Synchronous Servo Motor with Brake vacuum pump
Product Description
1.Product tyep
60# 220V 400W AC Permanent Magnet Synchronous Servo motor with brake;Encoder can be choosed according to your requirements; High-end motor application fields cover industrial robots, AGVs, intelligent factories, CNC, and 3C, among others.
2.OEM&ODM are all acceptable
3.Our advantages:
3.1Having an excellent R&D team,
3.2. RELIABILITY FIRST , QUALITY CONTROL MANAGEMENT FIRST.
3.3.SHORT LEAD TIME (Conventional products about one-week)
3.4 COST-EFFECTIVE (competitive price )
3.5 Certification:ISO9001, CE; and our products meet RoHS requirements.
3.6 With a one-year warranty (under normal use)
4.Product features
4.1. The entire series adopts a 5-pair pole scheme;
4.2. Compared to competitors in the same industry, the product size has a shorter advantage;
4.3. The rotor adopts embedded magnetic steel, without the risk of magnetic steel falling off;
4.4. Encoders can be matched with various types, and the company has its own encoder products for matching use
Compared to peers, it has supporting advantages.
4.5. The appearance of the motor is available in silver and black, with a focus on black.
5.Technical indicators
| Rated output power | 400 | W |
| Number of poles | 10 | P |
| rated voltage | 220 | VAC |
| Rated speed | 3000 | r/min |
| Maximum speed | 5000 | r/min |
| Rated torque | 1.27 | N.m |
| Instantaneous maximum torque | 4.46 | N.m |
| Rated Current | 2.1 | A(rms) |
| Instantaneous maximum current | 7.5 | A(rms) |
| Line back EMF | 38.4 | V/krpm |
| Torque coefficient | 0.635 | N.m/A |
| Moment of inertia | Kg.sq.m.10-4 | |
| Line resistance | 6.1 | ohm |
| Line inductance | 13.3 | mH |
| Brake rated voltage | 24V+2.4V | VDC |
| Brake rated power | 7.6 | W |
| Brake static torque | ≥1.5 | N.m |
| Brake moment of inertia | 0.587 | Kg.sq.m.10-4 |
| Weight | 1.3 | Kg |
| Feedback element | Optional | |
| Temperature sensor | NC |
6.Functional features
| Working hours | Continuous |
| Heat resistance | Class F |
| Body color | Black |
| Cooling method | Natural cooling |
| Vibration level | V15 |
| Connection method | Direct connection |
| Installation method | Flange installation |
| Excitation method | Permanent magnet |
| Protection method | Fully enclosed ,self-cooling IP65 (except shaft penetration) |
| Rotation method | Counterclockwise rotation(CCW) as seen from the extension end of the motor shaft |
7.Outside view
8.Dimensions
9.Model Explanation
10.Servo motor wiring definition
11.Company Profile
12.Development history
13.Motor overview
14.Certificate patent display
15.FAQ
Payments
1) We can accept EXW, FOB
2) Payment must be made before shipment.
3) Import duties, taxes and charges are not included in the item price or shipping charges. These charges are the buyer's responsibility.
Shipping
1) We only ship to your confirmed address. Please make sure your shipping address is correct before purchase.
2) Most orders will be shipped out within 3-7 working days CHINAMFG payment confirmation.
3) Shipping normally takes 7-25 working days. Most of the items will delivery in 2 weeks, while there will be a delay for something we cannot control (such as the bad weather). If it happens, just contact us, we will help you check and resolve any problem.
4) Please check the package CHINAMFG receipt, if there are some damages, please contact us immediately.
Feedback & Refund
1) Feedback is important to us, if you have any problem with our products, please contact us, our technician will give you useful advises.
2) When you have the parcel and not satisfied with the goods or it is other problem, please tell us immediately, and provide us a photo showing the detail.
3) Any reason requiring for all refund. Items must be in original condition and no physical damage. Buyer responsible for all shipping cost.
If you need more information, please contact with us. We will attach great importance to your any problems.Hope we could establish a long-term effective cooperation.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Household Appliances, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Excitation Mode: | Permanent Magnet |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 10 |
| Samples: |
US$ 85/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What safety precautions should be followed when working with brake motors?
Working with brake motors requires adherence to specific safety precautions to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the equipment. Brake motors involve electrical components and potentially hazardous mechanical operations, so it is essential to follow established safety guidelines. Here's a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with brake motors:
- Qualified Personnel: Only trained and qualified individuals should be allowed to work with brake motors. They should have a thorough understanding of electrical systems, motor operation, and safety procedures. Proper training ensures that personnel are familiar with the specific risks associated with brake motors and know how to handle them safely.
- Power Isolation: Before performing any maintenance or repair tasks on a brake motor, it is crucial to isolate the power supply to the motor. This can be achieved by disconnecting the power source and following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental re-energization. Power isolation eliminates the risk of electric shock and allows safe access to the motor without the danger of unexpected startup.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with brake motors, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn. This may include safety glasses, gloves, protective clothing, and hearing protection, depending on the specific hazards present. PPE helps safeguard against potential hazards such as flying debris, electrical shocks, and excessive noise, providing an additional layer of protection for personnel.
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate ventilation should be ensured when working with brake motors, especially in indoor environments. Ventilation helps dissipate heat generated by the motor and prevents the buildup of potentially harmful fumes or gases. Proper ventilation reduces the risk of overheating and improves air quality, creating a safer working environment.
- Safe Lifting and Handling: Brake motors can be heavy and require proper lifting and handling techniques to prevent injuries. When moving or installing a motor, personnel should use appropriate lifting equipment, such as cranes or hoists, and follow safe lifting practices. It is important to avoid overexertion, use proper body mechanics, and seek assistance when necessary to prevent strains or accidents.
- Protection Against Moving Parts: Brake motors may have rotating or moving parts that pose a risk of entanglement or crushing injuries. Guards and protective covers should be in place to prevent accidental contact with these hazardous areas. Personnel should never reach into or attempt to adjust the motor while it is in operation or without proper lockout/tagout procedures in place.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of brake motors are essential for their safe and reliable operation. Maintenance tasks should only be performed by qualified personnel following manufacturer recommendations. Before conducting any maintenance or inspection, the motor should be properly isolated and de-energized. Visual inspections, lubrication, and component checks should be carried out according to the motor's maintenance schedule to identify and address any potential issues before they escalate.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations when working with brake motors. This includes adhering to installation procedures, operating instructions, and maintenance practices specified by the manufacturer. Manufacturers provide specific safety instructions and precautions that are tailored to their equipment, ensuring safe and efficient operation when followed meticulously.
- Training and Awareness: Ongoing training and awareness programs should be implemented to keep personnel updated on safety practices and potential hazards associated with brake motors. This includes providing clear instructions, conducting safety meetings, and promoting a safety-conscious culture. Personnel should be encouraged to report any safety concerns or incidents to ensure continuous improvement of safety measures.
By following these safety precautions, personnel can mitigate risks and create a safer working environment when dealing with brake motors. Adhering to proper procedures, using appropriate PPE, ensuring power isolation, practicing safe lifting and handling, protecting against moving parts, conducting regular maintenance and inspections, and staying informed about manufacturer guidelines are all crucial steps in maintaining a safe and efficient work environment when working with brake motors.

Can you provide examples of machinery or equipment that frequently use brake motors?
In various industrial and manufacturing applications, brake motors are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment. These motors provide braking functionality and enhance the safety and control of rotating machinery. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that frequently utilize brake motors:
- Conveyor Systems: Brake motors are extensively used in conveyor systems, where they control the movement and stopping of conveyor belts. They ensure smooth and controlled starting, stopping, and positioning of material handling conveyors in industries such as logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing.
- Hoists and Cranes: Brake motors are employed in hoists and cranes to provide reliable load holding and controlled lifting operations. They ensure secure stopping and prevent unintended movement of loads during lifting, lowering, or suspension of heavy objects in construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and other settings.
- Elevators and Lifts: Brake motors are an integral part of elevator and lift systems. They facilitate controlled starting, stopping, and leveling of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and other structures.
- Metalworking Machinery: Brake motors are commonly used in metalworking machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. They enable precise control and stopping of rotating spindles, ensuring safe machining operations and preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled rotation.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Brake motors are found in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. They provide controlled stopping and precise positioning of printing cylinders, rollers, or packaging components, ensuring accurate printing, packaging, and labeling processes.
- Textile Machinery: In textile manufacturing, brake motors are used in various machinery, including spinning machines, looms, and winding machines. They enable controlled stopping and tension control of yarns, threads, or fabrics, enhancing safety and quality in textile production.
- Machine Tools: Brake motors are widely employed in machine tools such as grinders, saws, and machining centers. They enable controlled stopping and tool positioning, ensuring precise machining operations and minimizing the risk of tool breakage or workpiece damage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Brake motors are utilized in material handling equipment such as forklifts, pallet trucks, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). They provide controlled stopping and holding capabilities, enhancing the safety and stability of load transport and movement within warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
- Winches and Winders: Brake motors are commonly used in winches and winders for applications such as cable pulling, wire winding, or spooling operations. They ensure controlled stopping, load holding, and precise tension control, contributing to safe and efficient winching or winding processes.
- Industrial Fans and Blowers: Brake motors are employed in industrial fans and blowers used for ventilation, cooling, or air circulation purposes. They provide controlled stopping and prevent the fan or blower from freewheeling when power is turned off, ensuring safe operation and avoiding potential hazards.
These examples represent just a selection of the machinery and equipment where brake motors are frequently utilized. Brake motors are versatile components that enhance safety, control, and performance in numerous industrial applications, ensuring reliable stopping, load holding, and motion control in rotating machinery.

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here's a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-05-09
China Best Sales 370W 750W 1.1kw 1.5kw 2.2kw 3kw 3.7kw 5.5kw 7.5kw 3 Phase 220V Induction Electric Brake Motor vacuum pump connector
Product Description
Product Description
Aluminum shell 0.12kw-315kw three-phase asynchronous motor
The performance of YE2 series high-efficiency three-phase asynchronous motors conforms to the national standard GB/T11707.
YE2 series of high-efficiency motors are energy-saving and environmentally friendly, using new technologies, new processes and new materials, so that the efficiency index of the motor completely reaches the index level of IE2. The motor uses class F insulation, and the temperature rise of the whole series is assessed according to class B, which greatly improves Safety and reliability. It can be widely used in various mechanical transmission equipment such as machine tools, fans, pumps, compressors, packaging machinery, mining machinery, construction machinery and so on.
The power can meet 0.18KW-900kw, the normal voltage is 380v, and the voltage can be customized 415v 430v, etc., the speed has 2 poles, 4 poles, 6 poles and 8 poles.The normal frequency is 50hz, 60hz needs to be customized, the cooling method is ic411, the protection level is IP55, and the working system is S1.
Installation structure B3 foot ;B5 conventional flange ;B35 foot and conventional flange.
Motor Features:
1. Frame size:H56-355;
2. Power:0.12-315Kw;
3. Voltage: 380V;
4. Rated Frequency: 50 Hz / 60 Hz;
5. Poles: 2 / 4 / 6 / 8 / 10
6. Speed: 590 -2980 r/min
7. Ambient Temperature: -15°C-40°C
8. Model of CONEECTION: Y-Connection for 3 KW motor or less while Delta-Connection for 4 KW motor or more;
9. Mounting: B3; B5; B35; B14; B34;
10. Current: 1.5-465 A (AC);
11. Duty: continuous (S1);
12. Insulation Class: B;
13. Protection Class: IP44,IP54,IP55;
14. Frame material: aluminum body(56-132 frame), cast iron(71-355 frame)
15. Terminal box : Top or Side
16. Cooling Method: IC411 Standards;
17. Altitude: No more than 1,000 meters above sea level;
18. Packing: 63-112 frame be packaged by carton&pallets
132-355 frame be packaged by plywood case;
19. Certifications: CE, CCC, ISO9001: 2008
Installation Instructions
| Three-phase Asynchronous Electric Motor | |
| 1). Power: | 0.12KW-315KW; |
| 2). Frame: | H56 to 355; |
| 3). Shell: | cast iron body , aluminum body ; |
| 4). Pole: | 2/4/6/8 poles; |
| 5). Mounting arrangement: | B3/B5/B14/B35/B34 or other; |
| 6). Voltage: | 220V, 380V, 400V, 415V, 440V or on request (50Hz or 60Hz); |
| 7). Protection class: | IP54 / IP55 /IP65; |
| 8). Duty/Rating: | S1 (Continuous); |
| 9). Cooling method: | IC411 (SELF-FAN cooling); |
| 10). Insulation class: | F; |
| 11).Standard: | (IEC) EN60034-1 & EN1065714-1. |
Technical Data
technical parameter
|
Model |
Output
|
Full Load |
75%load |
50%load |
Ist/TN
|
Tst/TN |
Tmax/TN |
||||||
|
KW |
HP |
Current(A) |
Speed(r/min) |
Eff(%) |
Power factor |
Eff(%) |
Power factor |
Eff(%) |
Power factor |
||||
| 380V 50Hz Synchronous Speed 3000r/min(2 poles) | |||||||||||||
| MS56M1-2 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 2700 | 58.0 | 0.78 | 56.2 | 0.77 | 54.0 | 0.74 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 2.2 |
| MS56M2-2 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 2700 | 60.0 | 0.79 | 58.5 | 0.78 | 56.0 | 0.75 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 2.2 |
| MS63M1-2 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.53 | 2720 | 63.0 | 0.80 | 62.0 | 0.80 | 60.5 | 0.76 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 2.2 |
| MS63M2-2 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.63 | 2720 | 65.0 | 0.81 | 64.0 | 0.80 | 62.5 | 0.77 | 2.2 | 5.5 | 2.2 |
| MS71M1-2 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.99 | 2740 | 66.0 | 0.81 | 65.0 | 0.80 | 63.5 | 0.78 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 2.2 |
| MS71M2-2 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.40 | 2740 | 71.0 | 0.82 | 70.0 | 0.82 | 68.5 | 0.79 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 2.3 |
| MS80M1-2 | 0.75 | 1 | 1.83 | 2835 | 77.4 | 0.83 | 72.0 | 0.83 | 70.2 | 0.80 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 2.3 |
| MS80M2-2 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.58 | 2835 | 79.6 | 0.84 | 75.1 | 0.83 | 73.0 | 0.80 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS90S-2 | 1.5 | 2 | 3.43 | 2845 | 81.3 | 0.84 | 77.0 | 0.85 | 70.0 | 0.81 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS90L-2 | 2.2 | 3 | 4.85 | 2845 | 83.2 | 0.85 | 80.0 | 0.85 | 78.0 | 0.84 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS100L-2 | 3.0 | 4 | 6.31 | 2875 | 84.6 | 0.87 | 81.0 | 0.86 | 79.3 | 0.86 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS112M-2 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 8.10 | 2895 | 85.8 | 0.88 | 83.5 | 0.87 | 81.0 | 0.84 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| MS132S1-2 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 11.0 | 2905 | 87.0 | 0.88 | 84.3 | 0.89 | 83.0 | 0.84 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| MS132S2-2 | 7.5 | 10 | 14.9 | 2905 | 88.1 | 0.88 | 85.9 | 0.87 | 83.7 | 0.84 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| MS160M1-2 | 11 | 15 | 21.3 | 2935 | 89.4 | 0.89 | 86.8 | 0.89 | 84.1 | 0.84 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| MS160M2-2 | 15 | 20 | 28.8 | 2935 | 90.3 | 0.89 | 88.0 | 0.89 | 86.4 | 0.85 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| MS160L-2 | 18.5 | 25 | 34.7 | 2935 | 90.9 | 0.90 | 89.0 | 0.88 | 86.8 | 0.86 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| 380V 50Hz Synchronous Speed 1500/min(4poles) | |||||||||||||
| MS56M1-4 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.26 | 1300 | 53.0 | 0.70 | 51.8 | 0.65 | 50.0 | 0.53 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS56M2-4 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 1300 | 55.0 | 0.71 | 53.8 | 0.67 | 52.0 | 0.55 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS63M1-4 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 1310 | 57.0 | 0.72 | 56.1 | 0.69 | 53.9 | 0.57 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS63M2-4 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 1310 | 60.0 | 0.73 | 58.5 | 0.70 | 56.7 | 0.59 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS71M1-4 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.79 | 1330 | 65.0 | 0.74 | 62.4 | 0.73 | 59.3 | 0.59 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS71M2-4 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 1.12 | 1330 | 67.0 | 0.75 | 65.3 | 0.74 | 60.8 | 0.63 | 2.1 | 5.2 | 2.2 |
| MS80M1-4 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.57 | 1395 | 71.0 | 0.75 | 69.2 | 0.74 | 67.2 | 0.64 | 2.4 | 5.2 | 2.3 |
| MS80M2-4 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 2.03 | 1395 | 79.6 | 0.76 | 71.7 | 0.75 | 69.8 | 0.67 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 2.3 |
| MS90S-4 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.89 | 1405 | 81.4 | 0.77 | 73.1 | 0.75 | 70.8 | 0.67 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 2.3 |
| MS90L-4 | 1.5 | 2 | 3.70 | 1405 | 82.8 | 0.79 | 76.1 | 0.76 | 73.7 | 0.69 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 2.3 |
| MS100L1-4 | 2.2 | 3 | 5.16 | 1435 | 84.3 | 0.81 | 78.0 | 0.79 | 75.5 | 0.69 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS100L2-4 | 3.0 | 4 | 6.78 | 1435 | 85.5 | 0.82 | 79.9 | 0.78 | 77.5 | 0.70 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS112M-4 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 8.80 | 1445 | 86.6 | 0.82 | 81.9 | 0.79 | 79.6 | 0.70 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS132S-4 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 11.7 | 1445 | 87.7 | 0.83 | 82.8 | 0.81 | 80.4 | 0.73 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS132M-4 | 7 | 10 | 15.6 | 1445 | 88.7 | 0.84 | 84.8 | 0.82 | 82.6 | 0.74 | 2.3 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS160M-4 | 11 | 15 | 22.3 | 1465 | 89.8 | 0.84 | 85.8 | 0.83 | 83.8 | 0.75 | 2.2 | 7.0 | 2.3 |
| MS160L-4 | 15 | 20 | 30.1 | 1465 | 90.6 | 0.85 | 90.0 | 0.83 | 88.5 | 0.75 | 2.2 | 7.5 | 2.3 |
| 380V 50Hz Synchronous Speed 1500/min(6 Poles) | |||||||||||||
| MS71M1-6 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.74 | 850 | 56.0 | 0.66 | 54.6 | 0.66 | 53.0 | 0.65 | 1.9 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| MS71M2-6 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.95 | 850 | 59.0 | 0.68 | 57.5 | 0.68 | 56.1 | 0.62 | 1.9 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| MS80M1-6 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 1.30 | 895 | 62.0 | 0.70 | 60.5 | 0.69 | 59.1 | 0.64 | 1.9 | 4.7 | 2.0 |
| MS80M2-6 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.79 | 895 | 65.0 | 0.72 | 63.3 | 0.71 | 60.1 | 0.64 | 1.9 | 4.7 | 2.1 |
| MS90S-6 | 0.75 | 1 | 2.29 | 915 | 75.9 | 0.72 | 67.3 | 0.72 | 66.3 | 0.65 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 2.1 |
| MS90L-6 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 3.18 | 915 | 78.1 | 0.73 | 70.2 | 0.72 | 38.0 | 0.66 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 2.2 |
| MS100L-6 | 1.5 | 2 | 3.94 | 945 | 79.8 | 0.75 | 74.0 | 0.75 | 71.0 | 0.68 | 2.0 | 5.5 | 2.1 |
| MS112M-6 | 2.2 | 3 | 5.60 | 945 | 81.8 | 0.75 | 77.1 | 0.77 | 75.1 | 0.69 | 2.0 | 6.5 | 2.1 |
| MS132M1-6 | 3.0 | 4 | 7.40 | 965 | 83.3 | 0.76 | 78.9 | 0.77 | 76.1 | 0.69 | 2.1 | 6.5 | 2.1 |
| MS132M2-6 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 9.80 | 965 | 84.6 | 0.76 | 80.0 | 0.76 | 77.5 | 0.70 | 2.1 | 6.5 | 2.1 |
| MS160M-6 | 7.5 | 10 | 17.0 | 975 | 87.2 | 0.77 | 83.4 | 0.77 | 82.4 | 0.70 | 2.0 | 6.5 | 2.1 |
| MS160L-6 | 11 | 15 | 24.2 | 975 | 88.7 | 0.78 | 86.6 | 0.78 | 84.8 | 0.72 | 2.0 | 6.5 | 2.1 |
| 380V 50Hz Synchronous Speed 750min(8 Poles) | |||||||||||||
| MS80M1-8 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.88 | 630 | 51.0 | 0.61 | 47.9 | 0.52 | 44.6 | 0.54 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 1.9 |
| MS80M2-8 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 1.15 | 640 | 54.0 | 0.61 | 48.9 | 0.54 | 45.3 | 0.55 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 1.9 |
| MS90S-8 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 1.49 | 660 | 62.0 | 0.61 | 55.6 | 0.57 | 50.7 | 0.56 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 1.9 |
| MS90L-8 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 2.18 | 660 | 63.0 | 0.61 | 55.9 | 0.58 | 50.9 | 0.59 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| MS100L1-8 | 0.75 | 1 | 2.17 | 690 | 71.0 | 0.67 | 60.9 | 0.65 | 59.7 | 0.56 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| MS100L2-8 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 2.39 | 690 | 73.0 | 0.69 | 72.0 | 0.61 | 59.8 | 0.57 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| MS112M-8 | 1.5 | 2 | 4.50 | 680 | 75.0 | 0.69 | 74.2 | 0.64 | 59.8 | 0.58 | 1.8 | 5.0 | 2.0 |
| MS132S-8 | 2.2 | 3 | 6.00 | 710 | 78.0 | 0.71 | 77.2 | 0.61 | 60.1 | 0.58 | 1.8 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| MS132M-8 | 3.0 | 4 | 7.90 | 710 | 79.0 | 0.73 | 78.5 | 0.62 | 60.0 | 0.59 | 1.8 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| MS160M1-8 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 10.3 | 720 | 81.0 | 0.73 | 80.2 | 0.63 | 61.0 | 0.58 | 1.9 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| MS160M2-8 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 13.6 | 720 | 83.0 | 0.74 | 81.2 | 0.61 | 62.0 | 0.59 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
| MS160L-8 | 7.5 | 10 | 17.8 | 720 | 85.5 | 0.75 | 84.5 | 0.63 | 65.9 | 0.59 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 |
Detailed Photos
Our OEM Motors, Diesel generator sets ,Alternators are talior made to fit the OEM customer's application. Our based Engineering Design team work with you to ensure the motor meets your individual needs.
2 ,4,6 ,8 and 10 pole operation. with CE Approvals available
All Motors, Diesel generator sets ,Alternators may be designed for optional voltages and frequencies.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Variable Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 2 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors impact the overall productivity of manufacturing processes?
Brake motors have a significant impact on the overall productivity of manufacturing processes by enhancing operational efficiency, improving safety, and enabling precise control over motion. They play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and controlled movement, which is vital for the seamless operation of machinery and equipment. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors impact the overall productivity of manufacturing processes:
- Precise Control and Positioning: Brake motors enable precise control over the speed, acceleration, and deceleration of machinery and equipment. This precise control allows for accurate positioning, alignment, and synchronization of various components, resulting in improved product quality and reduced errors. The ability to precisely control the motion enhances the overall productivity of manufacturing processes by minimizing waste, rework, and downtime.
- Quick Deceleration and Stopping: Brake motors provide fast and controlled deceleration and stopping capabilities. This is particularly important in manufacturing processes that require frequent changes in speed or direction. The ability to rapidly decelerate and stop equipment allows for efficient handling of workpieces, quick tool changes, and seamless transitions between manufacturing steps. It reduces cycle times and improves overall productivity by minimizing unnecessary delays and optimizing throughput.
- Improved Safety: Brake motors enhance safety in manufacturing processes by providing reliable braking functionality. They help prevent coasting or unintended movement of equipment when power is cut off or during emergency situations. The braking capability of brake motors contributes to the safe operation of machinery, protects personnel, and prevents damage to equipment or workpieces. By ensuring a safe working environment, brake motors help maintain uninterrupted production and minimize the risk of accidents or injuries.
- Enhanced Equipment Performance: The integration of brake motors into manufacturing equipment improves overall performance. Brake motors work in conjunction with motor control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or servo systems, to optimize motor operation. This integration allows for efficient power utilization, reduced energy consumption, and improved responsiveness. By maximizing equipment performance, brake motors contribute to higher productivity, lower operational costs, and increased output.
- Reduced Downtime and Maintenance: Brake motors are designed for durability and reliability, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and minimizing downtime. The robust construction and high-quality components of brake motors ensure long service life and consistent performance. This reliability translates into fewer unplanned shutdowns, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved overall equipment availability. By minimizing downtime and maintenance-related interruptions, brake motors contribute to increased productivity and manufacturing efficiency.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Brake motors offer flexibility and adaptability in manufacturing processes. They can be integrated into various types of machinery and equipment, spanning different industries and applications. Brake motors can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as adjusting brake torque or incorporating specific control algorithms. This adaptability allows manufacturers to optimize their processes, accommodate changing production needs, and increase overall productivity.
In summary, brake motors impact the overall productivity of manufacturing processes by providing precise control and positioning, enabling quick deceleration and stopping, improving safety, enhancing equipment performance, reducing downtime and maintenance, and offering flexibility and adaptability. Their role in ensuring smooth and controlled movement, combined with their reliable braking functionality, contributes to efficient and seamless manufacturing operations, ultimately leading to increased productivity, improved product quality, and cost savings.

What maintenance practices are essential for extending the lifespan of a brake motor?
Maintaining a brake motor properly is crucial for extending its lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance practices help prevent premature wear, identify potential issues, and address them promptly. Here are some essential maintenance practices for extending the lifespan of a brake motor:
- Cleanliness: Keeping the brake motor clean is important to prevent the accumulation of dirt, dust, or debris that can affect its performance. Regularly inspect the motor and clean it using appropriate cleaning methods and materials, ensuring that the power is disconnected before performing any cleaning tasks.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the brake motor's moving parts is essential to minimize friction and reduce wear and tear. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the type of lubricant to use and the frequency of lubrication. Ensure that the lubrication points are accessible and apply the lubricant in the recommended amounts.
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections of the brake motor are necessary to identify any signs of damage, loose connections, or abnormal wear. Check for any loose or damaged components, such as bolts, cables, or connectors. Inspect the brake pads or discs for wear and ensure they are properly aligned. If any issues are detected, take appropriate action to address them promptly.
- Brake Adjustment: Periodically check and adjust the brake mechanism of the motor to ensure it maintains proper braking performance. This may involve adjusting the brake pads, ensuring proper clearance, and verifying that the braking force is sufficient. Improper brake adjustment can lead to excessive wear, reduced stopping power, or safety hazards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring the operating temperature of the brake motor is important to prevent overheating and thermal damage. Ensure that the motor is not subjected to excessive ambient temperatures or overloaded conditions. If the motor becomes excessively hot, investigate the cause and take corrective measures, such as improving ventilation or reducing the load.
- Vibration Analysis: Periodic vibration analysis can help detect early signs of mechanical problems or misalignment in the brake motor. Using specialized equipment or vibration monitoring systems, measure and analyze the motor's vibration levels. If abnormal vibrations are detected, investigate and address the underlying issues to prevent further damage.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the electrical connections of the brake motor to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or faulty connections can lead to power issues, motor malfunctions, or electrical hazards. Tighten any loose connections and clean any corrosion using appropriate methods and materials.
- Testing and Calibration: Perform periodic testing and calibration of the brake motor to verify its performance and ensure it operates within the specified parameters. This may involve conducting load tests, verifying braking force, or checking the motor's speed and torque. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines or consult with qualified technicians for proper testing and calibration procedures.
- Documentation and Record-keeping: Maintain a record of all maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and any relevant information related to the brake motor. This documentation helps track the maintenance history, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks effectively. It also serves as a reference for warranty claims or troubleshooting purposes.
- Professional Servicing: In addition to regular maintenance tasks, consider scheduling professional servicing and inspections by qualified technicians. They can perform comprehensive checks, identify potential issues, and perform specialized maintenance procedures that require expertise or specialized tools. Professional servicing can help ensure thorough maintenance and maximize the lifespan of the brake motor.
By following these essential maintenance practices, brake motor owners can enhance the lifespan of the motor, reduce the risk of unexpected failures, and maintain its optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only extends the motor's lifespan but also contributes to safe operation, energy efficiency, and overall reliability.

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here's a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2024-05-02
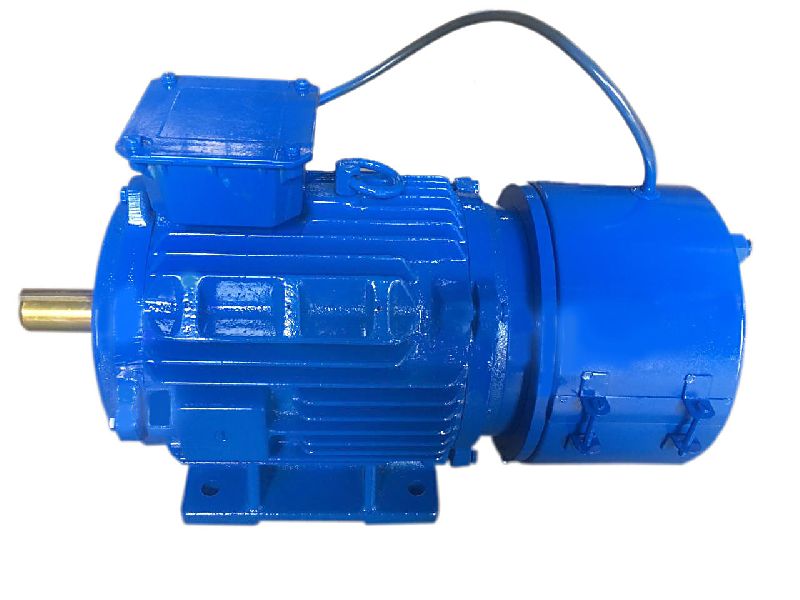
China Best Sales AC Gear Motor Three or Single Phase 110V 220V 380V Mini AC Motor with Brake vacuum pump and compressor
Product Description
Product specifications
The following are the specifications that our company's Micro AC gear motors 180w can achieved. You can also contact us to tell us the power, voltage, torque and other parameters you need. We can accept and customize. and You can also contact us for drawings and detailed parameters.
| Band name | Lunyee |
| Out Power | 180w |
| Dimension | 90mm |
| Voltage | 110v |
| Frequency | 50Hz 60Hz |
| Phase | Single phase |
| Current | 4.423 A |
| Rated speed | 1350/1680 r/min |
| Starting torque | 1.330/1.665 N.M |
| Rated torqur | 1.571/1.273 N.M |
| Rated time | 30 minutes |
| Capacitor | 25/250 uf/VAC |
| Motor Shaft type | Pinion shaft Round shaft Keyway |
| Accessories that can be added | gear box Terminal box w/fan w/ forced fan eleceromagnetic brake thermally |
| Micro ac gear motor type | Induction motor Reversible motor Torque motor Speed control motor Right angle gear motor Brake motor |
Product Features:
High efficiency
High torque Low speed
Low noise Long life Strong reliability
Running smoothly
Brushless environmental protection
Simple structure easy to use
Factory supplier best price
Suitable for extreme environments
Wide range of applications
product details
1.AC Gear Motor
Compact structure, good sealing performance, low noise, long life,low operating temperature Adjustable speed, reversible, CHINAMFG and reverse
2.All Copper Coil
All copper coil, fast heat dissipation, life is 10 times that of ordinary coil
3.High precision hard tooth surface
The gear has high precision, high hardness, anti-rust treatment, waterproof and quiet, long life
Application
AC gear motor widely used in Industrial equipment, machine tools, agricultural appliances, commercial office, medical equipment, household appliances, aviation and other fields. Such as treadmill, sewing machine, meat grinder , tortilla press maker, Apparel Machine, Textile Machine, Metal Coating Machinery, Pumps, Sprayers, heavy mine equipment, Packing Machine, nebulizer, table fan, Face Mask Machine, Rehabilitation Therapy Supplies, refrigerator, Air Purifiers, Fermenting Equipment. and many more.
Company Certifaction
About us:
ZheJiang CHINAMFG Industries Co., Limited. company, is the recognized top manufacturer of industrial humidification system inChina. Our factory has 3 large workshops, covering 3,000 square meter area. We have more than 100 employees, equip with professional R&D team, reliable workers and efficient sales service team. Green focus on research and development, manufacture, and sale of humidifying, air cooling, dedusting, dehumidifying and energy saving equipment. Our company is evolving as the change of customers' needs, we are committed to developing and engineering new technology to best suit our customers' demands. So far, we have got many patents on highly advanced and efficient humidifier designs.Working with Green, you will enjoy the latest and most advanced technology and kindest service.
Our Mine Product:
DC/AC motor, stepper motor, gearbox, CNC engraving machine, industrial humidifier.
Our Services:
Each of our products will undergo rigorous testing before leaving the factory. We will provide you with professional designs and solutions, high-quality products and high-quality services according to your needs. If you have any questions, please feel free to
contact us. We will serve you immediately.
Packing &Shipping
Inside : Plastic bags with Chemical Desiccant For Gear Housing
Middle : Individual Carton packaging Outside : Wooden Box
Shipment: TNT, DHL, UPS, FedEx,EMS etc.Or use the shipment your specified.
Strict product packaging ensures that the product is not damaged during transportation.
FAQ
Q1 Are you a manufacturer or a trading company?
We are a motor in China.
Q2 What's your warranty?
One-year.
Q3 Can you give more discounts if more quantity and how many?
We can afford discounts and rate based on updated quantity.
Q4 Can you make OEM/ODM order?
Yes, we have rich experience on OEM/ODM order.
Q5 Delivery
Sample can be afforded within 5-7days and volume order can be finished within 15-20days.
Q6 About sample?
Available.
Q7 Which of payments you support?
T/T, L/C,PAYPAL, CREDIT CARD.
Q8 Which of transportations you support?
Sea, Air cargo, Train, DHL/FEDEX/UPS/TNT.
Q9 What you can do if we still have worry on your product?
We can afford sample for testing, if approval then negotiate cooperation later.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Variable Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Driving, Control |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors handle variations in brake torque and response time?
Brake motors are designed to handle variations in brake torque and response time to ensure reliable and efficient braking performance. These variations can arise due to different operating conditions, load characteristics, or specific application requirements. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors handle variations in brake torque and response time:
- Brake Design and Construction: The design and construction of brake systems in brake motors play a crucial role in handling variations in brake torque and response time. Brake systems typically consist of brake pads or shoes that press against a brake disc or drum to generate frictional forces and provide braking action. The materials used for the brake components, such as brake linings, can be selected or designed to offer a wide range of torque capacities and response characteristics. By choosing the appropriate materials and optimizing the brake system design, brake motors can accommodate variations in torque requirements and response times.
- Brake Control Mechanisms: Brake motors employ different control mechanisms to manage brake torque and response time. These mechanisms can be mechanical, electrical, or a combination of both. Mechanical control mechanisms often utilize springs or levers to apply and release the brake, while electrical control mechanisms rely on electromagnets or solenoids to engage or disengage the brake. The control mechanisms can be adjusted or configured to modulate the brake torque and response time based on the specific needs of the application.
- Brake Torque Adjustments: Brake motors may offer provisions for adjusting the brake torque to accommodate variations in load requirements. This can be achieved through the selection of different brake linings or by adjusting the spring tension or magnetic force within the brake system. By modifying the brake torque, brake motors can provide the necessary braking force to meet the demands of different operating conditions or load characteristics.
- Response Time Optimization: Brake motors can be engineered to optimize the response time of the braking system. The response time refers to the time it takes for the brake to engage or disengage once the control signal is applied. Several factors can influence the response time, including the design of the control mechanism, the characteristics of the brake linings, and the braking system's overall dynamics. By fine-tuning these factors, brake motors can achieve faster or slower response times as required by the application, ensuring effective and timely braking action.
- Electronic Control Systems: In modern brake motors, electronic control systems are often employed to enhance the flexibility and precision of brake torque and response time adjustments. These systems utilize sensors, feedback mechanisms, and advanced control algorithms to monitor and regulate the brake performance. Electronic control allows for real-time adjustments and precise control of the brake torque and response time, making brake motors more adaptable to variations in operating conditions and load requirements.
By combining appropriate brake design and construction, control mechanisms, torque adjustments, response time optimization, and electronic control systems, brake motors can effectively handle variations in brake torque and response time. This enables them to provide reliable and efficient braking performance across a wide range of operating conditions, load characteristics, and application requirements.
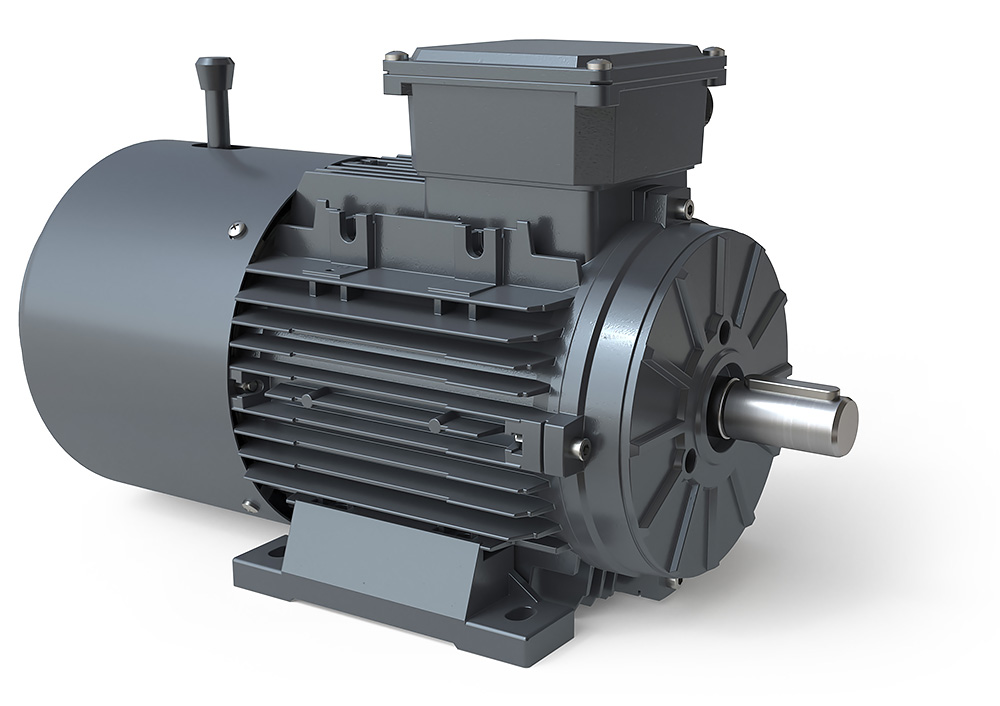
What factors should be considered when selecting the right brake motor for a task?
When selecting the right brake motor for a task, several factors should be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the specific application requirements. These factors help determine the suitability of the brake motor for the intended task and play a crucial role in achieving efficient and reliable operation. Here's a detailed explanation of the key factors that should be considered when selecting a brake motor:
1. Load Characteristics: The characteristics of the load being driven by the brake motor are essential considerations. Factors such as load size, weight, and inertia influence the torque, power, and braking requirements of the motor. It is crucial to accurately assess the load characteristics to select a brake motor with the appropriate power rating, torque capacity, and braking capability to handle the specific load requirements effectively.
2. Stopping Requirements: The desired stopping performance of the brake motor is another critical factor to consider. Different applications may have specific stopping time, speed, or precision requirements. The brake motor should be selected based on its ability to meet these stopping requirements, such as adjustable braking torque, controlled response time, and stability during stopping. Understanding the desired stopping behavior is crucial for selecting a brake motor that can provide the necessary control and accuracy.
3. Environmental Conditions: The operating environment in which the brake motor will be installed plays a significant role in its selection. Factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, vibration, and corrosive substances can affect the performance and lifespan of the motor. It is essential to choose a brake motor that is designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of the application, ensuring reliable and durable operation over time.
4. Mounting and Space Constraints: The available space and mounting requirements should be considered when selecting a brake motor. The physical dimensions and mounting options of the motor should align with the space constraints and mounting configuration of the application. It is crucial to ensure that the brake motor can be properly installed and integrated into the existing machinery or system without compromising the performance or safety of the overall setup.
5. Power Supply: The availability and characteristics of the power supply should be taken into account. The voltage, frequency, and power quality of the electrical supply should match the specifications of the brake motor. It is important to consider factors such as single-phase or three-phase power supply, voltage fluctuations, and compatibility with other electrical components to ensure proper operation and avoid electrical issues or motor damage.
6. Brake Type and Design: Different brake types, such as electromagnetic brakes or spring-loaded brakes, offer specific advantages and considerations. The choice of brake type should align with the requirements of the application, taking into account factors such as braking torque, response time, and reliability. The design features of the brake, such as braking surface area, cooling methods, and wear indicators, should also be evaluated to ensure efficient and long-lasting braking performance.
7. Regulatory and Safety Standards: Compliance with applicable regulatory and safety standards is crucial when selecting a brake motor. Depending on the industry and application, specific standards and certifications may be required. It is essential to choose a brake motor that meets the necessary standards and safety requirements to ensure the protection of personnel, equipment, and compliance with legal obligations.
8. Cost and Lifecycle Considerations: Finally, the cost-effectiveness and lifecycle considerations should be evaluated. This includes factors such as initial investment, maintenance requirements, expected lifespan, and availability of spare parts. It is important to strike a balance between upfront costs and long-term reliability, selecting a brake motor that offers a favorable cost-to-performance ratio and aligns with the expected lifecycle and maintenance budget.
Considering these factors when selecting a brake motor helps ensure that the chosen motor is well-suited for the intended task, provides reliable and efficient operation, and meets the specific requirements of the application. Proper evaluation and assessment of these factors contribute to the overall success and performance of the brake motor in its designated task.

How do brake motors ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment?
Brake motors are designed to ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment by employing specific braking mechanisms. These mechanisms are integrated into the motor to provide efficient and precise stopping capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors achieve controlled and rapid stopping:
1. Electromagnetic Brakes: Many brake motors utilize electromagnetic brakes as the primary braking mechanism. These brakes consist of an electromagnetic coil and a brake disc or plate. When the power to the motor is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field that attracts the brake disc or plate, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. The strength of the magnetic field and the design of the brake determine the stopping torque and speed, allowing for controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
2. Spring-Loaded Brakes: Some brake motors employ spring-loaded brakes. These brakes consist of a spring that applies pressure on the brake disc or plate to create friction and stop the rotation. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the spring is released, pressing the brake disc against a stationary surface and generating braking force. The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick engagement of the brake, resulting in rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is another technique used in brake motors to achieve controlled stopping. It involves converting the kinetic energy of the rotating equipment into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the motor acts as a generator, and the electrical energy generated by the rotating equipment is converted into heat through the braking system. This dissipation of energy slows down and stops the rotation of the equipment in a controlled manner.
4. Control Systems: Brake motors are often integrated with control systems that enable precise control over the braking process. These control systems allow for adjustable braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, depending on the specific requirements of the application. By adjusting these parameters, operators can achieve the desired level of control and stopping performance, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
5. Coordinated Motor and Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with careful consideration of the motor and brake compatibility. The motor's characteristics, such as torque, speed, and power rating, are matched with the braking system's capabilities to ensure optimal performance. This coordinated design ensures that the brake can effectively stop the motor within the desired time frame and with the necessary braking force, achieving controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
Overall, brake motors employ electromagnetic brakes, spring-loaded brakes, dynamic braking, and control systems to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment. These braking mechanisms, combined with coordinated motor and brake design, enable precise control over the stopping process, ensuring the safety of operators, protecting equipment from damage, and maintaining operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-04-30
China OEM 220V Single Phase AC Brake Reversible Gear Motor with Fan vacuum pump
Product Description
Specifications
1) Dimensions of device: 42mm, 60mm, 70mm, 80mm, 90mm, 104mm
2) Power: 6W, 15W, 25W, 40W, 60W, 90W, 120W, 140W
3) Voltage Poles: Single-Phase 100V 50/60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 2P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 110V 50/60Hz 2P
Single-Phase 110V,120V 60Hz 4P
Single-Phase 220V,120V 60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 200/220/230V 50/60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 380/415V 50/60Hz 4P
Three-Phase 200/220/230V 50/60Hz 2P
Three-Phase 380/415V 50/60Hz 2P
4) Gear ratio of the Gear Head: 3, 3.6, 5, 6, 7.5, 9, 12.5, 15, 18, 25, 30, 36, 50, 60,75,90,100,120,150,180,250
We are specialized in Mini AC Gear Motor. Our main products are used for MachineTools, Textile Machinery, Medical Appliance, Conveying Machine, Printing Mechanism, Food Machinery, Vending Machine, Packing Machinery, Gumming Machine and so on. We offer customers with top quality products and fine service. Please contact us if you have any question or inquiry.
Our reduction geared motor Advantage
1,reasonable price with excellent quality
2,delivery in time
3,safe ,reliable ,economical and durable
4,stable transmission ,quiet operation
5,smooth running and low noise
6,nice appearance ,durable service life
7,high heat-radiating efficiency ,high carrying ability
8,each gearbox must be tested before packing
9.reply in high efficiency during 1 working day
10. professional to produce gearbox and electric motor .
FAQ
1, Q:what\'s your MOQ for ac gearbox motor ?
A: 1pc is ok for each type electric gear box motor
2, Q: What about your warranty for your induction speed reducer motor ?
A: 1 year ,but except man-made destroyed
3, Q: which payment way you can accept ?
A: TT, western union .
4, Q: how about your payment way ?
A: 100%payment in advanced less $5000 ,30% payment in advanced payment , 70% payment before sending over $5000.
5, Q: how about your packing of speed reduction motor ?
A: plywood case ,if size is small ,we will pack with pallet for less 1 container
6, Q: What information should be given, if I buy electric helical geared motor from you ?
A: rated power, ratio or output speed,type ,voltage , mounting way , quantity , if more is better ,
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industrial |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Three-Phase |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Number of Poles: | 4 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What safety precautions should be followed when working with brake motors?
Working with brake motors requires adherence to specific safety precautions to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the equipment. Brake motors involve electrical components and potentially hazardous mechanical operations, so it is essential to follow established safety guidelines. Here's a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be followed when working with brake motors:
- Qualified Personnel: Only trained and qualified individuals should be allowed to work with brake motors. They should have a thorough understanding of electrical systems, motor operation, and safety procedures. Proper training ensures that personnel are familiar with the specific risks associated with brake motors and know how to handle them safely.
- Power Isolation: Before performing any maintenance or repair tasks on a brake motor, it is crucial to isolate the power supply to the motor. This can be achieved by disconnecting the power source and following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental re-energization. Power isolation eliminates the risk of electric shock and allows safe access to the motor without the danger of unexpected startup.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with brake motors, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn. This may include safety glasses, gloves, protective clothing, and hearing protection, depending on the specific hazards present. PPE helps safeguard against potential hazards such as flying debris, electrical shocks, and excessive noise, providing an additional layer of protection for personnel.
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate ventilation should be ensured when working with brake motors, especially in indoor environments. Ventilation helps dissipate heat generated by the motor and prevents the buildup of potentially harmful fumes or gases. Proper ventilation reduces the risk of overheating and improves air quality, creating a safer working environment.
- Safe Lifting and Handling: Brake motors can be heavy and require proper lifting and handling techniques to prevent injuries. When moving or installing a motor, personnel should use appropriate lifting equipment, such as cranes or hoists, and follow safe lifting practices. It is important to avoid overexertion, use proper body mechanics, and seek assistance when necessary to prevent strains or accidents.
- Protection Against Moving Parts: Brake motors may have rotating or moving parts that pose a risk of entanglement or crushing injuries. Guards and protective covers should be in place to prevent accidental contact with these hazardous areas. Personnel should never reach into or attempt to adjust the motor while it is in operation or without proper lockout/tagout procedures in place.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of brake motors are essential for their safe and reliable operation. Maintenance tasks should only be performed by qualified personnel following manufacturer recommendations. Before conducting any maintenance or inspection, the motor should be properly isolated and de-energized. Visual inspections, lubrication, and component checks should be carried out according to the motor's maintenance schedule to identify and address any potential issues before they escalate.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and recommendations when working with brake motors. This includes adhering to installation procedures, operating instructions, and maintenance practices specified by the manufacturer. Manufacturers provide specific safety instructions and precautions that are tailored to their equipment, ensuring safe and efficient operation when followed meticulously.
- Training and Awareness: Ongoing training and awareness programs should be implemented to keep personnel updated on safety practices and potential hazards associated with brake motors. This includes providing clear instructions, conducting safety meetings, and promoting a safety-conscious culture. Personnel should be encouraged to report any safety concerns or incidents to ensure continuous improvement of safety measures.
By following these safety precautions, personnel can mitigate risks and create a safer working environment when dealing with brake motors. Adhering to proper procedures, using appropriate PPE, ensuring power isolation, practicing safe lifting and handling, protecting against moving parts, conducting regular maintenance and inspections, and staying informed about manufacturer guidelines are all crucial steps in maintaining a safe and efficient work environment when working with brake motors.

Can you provide examples of machinery or equipment that frequently use brake motors?
In various industrial and manufacturing applications, brake motors are commonly used in a wide range of machinery and equipment. These motors provide braking functionality and enhance the safety and control of rotating machinery. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that frequently utilize brake motors:
- Conveyor Systems: Brake motors are extensively used in conveyor systems, where they control the movement and stopping of conveyor belts. They ensure smooth and controlled starting, stopping, and positioning of material handling conveyors in industries such as logistics, warehousing, and manufacturing.
- Hoists and Cranes: Brake motors are employed in hoists and cranes to provide reliable load holding and controlled lifting operations. They ensure secure stopping and prevent unintended movement of loads during lifting, lowering, or suspension of heavy objects in construction sites, ports, manufacturing facilities, and other settings.
- Elevators and Lifts: Brake motors are an integral part of elevator and lift systems. They facilitate controlled starting, stopping, and leveling of elevators, ensuring passenger safety and smooth operation in commercial buildings, residential complexes, and other structures.
- Metalworking Machinery: Brake motors are commonly used in metalworking machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines. They enable precise control and stopping of rotating spindles, ensuring safe machining operations and preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled rotation.
- Printing and Packaging Machinery: Brake motors are found in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. They provide controlled stopping and precise positioning of printing cylinders, rollers, or packaging components, ensuring accurate printing, packaging, and labeling processes.
- Textile Machinery: In textile manufacturing, brake motors are used in various machinery, including spinning machines, looms, and winding machines. They enable controlled stopping and tension control of yarns, threads, or fabrics, enhancing safety and quality in textile production.
- Machine Tools: Brake motors are widely employed in machine tools such as grinders, saws, and machining centers. They enable controlled stopping and tool positioning, ensuring precise machining operations and minimizing the risk of tool breakage or workpiece damage.
- Material Handling Equipment: Brake motors are utilized in material handling equipment such as forklifts, pallet trucks, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). They provide controlled stopping and holding capabilities, enhancing the safety and stability of load transport and movement within warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing facilities.
- Winches and Winders: Brake motors are commonly used in winches and winders for applications such as cable pulling, wire winding, or spooling operations. They ensure controlled stopping, load holding, and precise tension control, contributing to safe and efficient winching or winding processes.
- Industrial Fans and Blowers: Brake motors are employed in industrial fans and blowers used for ventilation, cooling, or air circulation purposes. They provide controlled stopping and prevent the fan or blower from freewheeling when power is turned off, ensuring safe operation and avoiding potential hazards.
These examples represent just a selection of the machinery and equipment where brake motors are frequently utilized. Brake motors are versatile components that enhance safety, control, and performance in numerous industrial applications, ensuring reliable stopping, load holding, and motion control in rotating machinery.

How do brake motors ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment?
Brake motors are designed to ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment by employing specific braking mechanisms. These mechanisms are integrated into the motor to provide efficient and precise stopping capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors achieve controlled and rapid stopping:
1. Electromagnetic Brakes: Many brake motors utilize electromagnetic brakes as the primary braking mechanism. These brakes consist of an electromagnetic coil and a brake disc or plate. When the power to the motor is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field that attracts the brake disc or plate, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. The strength of the magnetic field and the design of the brake determine the stopping torque and speed, allowing for controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
2. Spring-Loaded Brakes: Some brake motors employ spring-loaded brakes. These brakes consist of a spring that applies pressure on the brake disc or plate to create friction and stop the rotation. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the spring is released, pressing the brake disc against a stationary surface and generating braking force. The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick engagement of the brake, resulting in rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is another technique used in brake motors to achieve controlled stopping. It involves converting the kinetic energy of the rotating equipment into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the motor acts as a generator, and the electrical energy generated by the rotating equipment is converted into heat through the braking system. This dissipation of energy slows down and stops the rotation of the equipment in a controlled manner.
4. Control Systems: Brake motors are often integrated with control systems that enable precise control over the braking process. These control systems allow for adjustable braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, depending on the specific requirements of the application. By adjusting these parameters, operators can achieve the desired level of control and stopping performance, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
5. Coordinated Motor and Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with careful consideration of the motor and brake compatibility. The motor's characteristics, such as torque, speed, and power rating, are matched with the braking system's capabilities to ensure optimal performance. This coordinated design ensures that the brake can effectively stop the motor within the desired time frame and with the necessary braking force, achieving controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
Overall, brake motors employ electromagnetic brakes, spring-loaded brakes, dynamic braking, and control systems to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment. These braking mechanisms, combined with coordinated motor and brake design, enable precise control over the stopping process, ensuring the safety of operators, protecting equipment from damage, and maintaining operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-04-12
China wholesaler Universal Hot Sale with brake 125W bldc hub electric 220V DC motor vacuum pump engine
Product Description
Product Description:
Gear Motor-Torque Table Allowance Torque Unit:Upside (N.m)/Belowside (kgf.cm)
•Gearhead and Intermediate gearhead are sold separately.
•Enter the reduction ratio into the blank() within the model name.
•The speed is calculated by dividing the motor's synchronous speed by the reduction ratio. The actual speed is 2%~20% less than the displayed value, depending on the size of the load.
•To reduce the speed beyond the reduction ratio in the following table, attach an intermediate gearhead (reduction ratio: 10) between the reducer and motor. In that case, the permissible torque is 20N.m.
|
Type Motor/Gearhead |
Gear Ratio |
3 |
3.6 |
5 |
6 |
7.5 |
9 |
12.5 |
15 |
18 |
25 |
30 |
36 |
50 |
60 |
75 |
90 |
100 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
|
Speed r/min |
866 |
722 |
520 |
433 |
346 |
288 |
208 |
173 |
144 |
104 |
86 |
72 |
52 |
43 |
34 |
28 |
26 |
21 |
17 |
14 |
|
| Z5D120-24GU-M(5GU180KB) |
5GU()RC/ 5GU()RT |
0.87 |
1.04 |
1.45 |
1.74 |
2.41 |
5.44 |
4.02 |
4.82 |
5.78 |
8.03 |
9.64 |
10.4 |
14.5 |
17.4 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
8.87 |
10.6 |
14.8 |
17.7 |
24.6 |
55.5 |
41.0 |
48.2 |
59.0 |
81.9 |
98.3 |
106 |
148 |
177 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
Dimensions(Unit:mm):
Company Information
FAQ
Q: What're your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What's your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Please contact us if you have detailed requests, thank you () /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brushless |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC, CCC, CE, RoHS, UL |
| Commutation: | Brushless |
| Transport Package: | Cnt |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can brake motors be used in conjunction with other motion control methods?
Yes, brake motors can be used in conjunction with other motion control methods to achieve precise and efficient control over mechanical systems. Brake motors provide braking functionality, while other motion control methods offer various means of controlling the speed, position, and acceleration of the system. Combining brake motors with other motion control methods allows for enhanced overall system performance and versatility. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be used in conjunction with other motion control methods:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Brake motors can be used in conjunction with VFDs, which are electronic devices that control the speed and torque of an electric motor. VFDs enable precise speed control, acceleration, and deceleration of the motor by adjusting the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. By incorporating a brake motor with a VFD, the system benefits from both the braking capability of the motor and the advanced speed control provided by the VFD.
- Servo Systems: Servo systems are motion control systems that utilize servo motors and feedback mechanisms to achieve highly accurate control over position, velocity, and torque. In certain applications where rapid and precise positioning is required, brake motors can be used in conjunction with servo systems. The brake motor provides the braking function when the system needs to hold position or decelerate rapidly, while the servo system controls the dynamic motion and positioning tasks.
- Stepper Motor Control: Stepper motors are widely used in applications that require precise control over position and speed. Brake motors can be utilized alongside stepper motor control systems to provide braking functionality when the motor needs to hold position or prevent undesired movement. This combination allows for improved stability and control over the stepper motor system, especially in applications where holding torque and quick deceleration are important.
- Hydraulic or Pneumatic Systems: In some industrial applications, hydraulic or pneumatic systems are used for motion control. Brake motors can be integrated into these systems to provide additional braking capability when needed. For example, a brake motor can be employed to hold a specific position or provide emergency braking in a hydraulic or pneumatic actuator system, enhancing safety and control.
- Control Algorithms and Systems: Brake motors can also be utilized in conjunction with various control algorithms and systems to achieve specific motion control objectives. These control algorithms can include closed-loop feedback control, PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control, or advanced motion control algorithms. By incorporating a brake motor into the system, the control algorithms can utilize the braking functionality to enhance overall system performance and stability.
The combination of brake motors with other motion control methods offers a wide range of possibilities for achieving precise, efficient, and safe control over mechanical systems. Whether it is in conjunction with VFDs, servo systems, stepper motor control, hydraulic or pneumatic systems, or specific control algorithms, brake motors can complement and enhance the functionality of other motion control methods. This integration allows for customized and optimized control solutions to meet the specific requirements of diverse applications.

What maintenance practices are essential for extending the lifespan of a brake motor?
Maintaining a brake motor properly is crucial for extending its lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance practices help prevent premature wear, identify potential issues, and address them promptly. Here are some essential maintenance practices for extending the lifespan of a brake motor:
- Cleanliness: Keeping the brake motor clean is important to prevent the accumulation of dirt, dust, or debris that can affect its performance. Regularly inspect the motor and clean it using appropriate cleaning methods and materials, ensuring that the power is disconnected before performing any cleaning tasks.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the brake motor's moving parts is essential to minimize friction and reduce wear and tear. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the type of lubricant to use and the frequency of lubrication. Ensure that the lubrication points are accessible and apply the lubricant in the recommended amounts.
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections of the brake motor are necessary to identify any signs of damage, loose connections, or abnormal wear. Check for any loose or damaged components, such as bolts, cables, or connectors. Inspect the brake pads or discs for wear and ensure they are properly aligned. If any issues are detected, take appropriate action to address them promptly.
- Brake Adjustment: Periodically check and adjust the brake mechanism of the motor to ensure it maintains proper braking performance. This may involve adjusting the brake pads, ensuring proper clearance, and verifying that the braking force is sufficient. Improper brake adjustment can lead to excessive wear, reduced stopping power, or safety hazards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring the operating temperature of the brake motor is important to prevent overheating and thermal damage. Ensure that the motor is not subjected to excessive ambient temperatures or overloaded conditions. If the motor becomes excessively hot, investigate the cause and take corrective measures, such as improving ventilation or reducing the load.
- Vibration Analysis: Periodic vibration analysis can help detect early signs of mechanical problems or misalignment in the brake motor. Using specialized equipment or vibration monitoring systems, measure and analyze the motor's vibration levels. If abnormal vibrations are detected, investigate and address the underlying issues to prevent further damage.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the electrical connections of the brake motor to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or faulty connections can lead to power issues, motor malfunctions, or electrical hazards. Tighten any loose connections and clean any corrosion using appropriate methods and materials.
- Testing and Calibration: Perform periodic testing and calibration of the brake motor to verify its performance and ensure it operates within the specified parameters. This may involve conducting load tests, verifying braking force, or checking the motor's speed and torque. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines or consult with qualified technicians for proper testing and calibration procedures.
- Documentation and Record-keeping: Maintain a record of all maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and any relevant information related to the brake motor. This documentation helps track the maintenance history, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks effectively. It also serves as a reference for warranty claims or troubleshooting purposes.
- Professional Servicing: In addition to regular maintenance tasks, consider scheduling professional servicing and inspections by qualified technicians. They can perform comprehensive checks, identify potential issues, and perform specialized maintenance procedures that require expertise or specialized tools. Professional servicing can help ensure thorough maintenance and maximize the lifespan of the brake motor.
By following these essential maintenance practices, brake motor owners can enhance the lifespan of the motor, reduce the risk of unexpected failures, and maintain its optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only extends the motor's lifespan but also contributes to safe operation, energy efficiency, and overall reliability.

How do brake motors ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment?
Brake motors are designed to ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment by employing specific braking mechanisms. These mechanisms are integrated into the motor to provide efficient and precise stopping capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors achieve controlled and rapid stopping:
1. Electromagnetic Brakes: Many brake motors utilize electromagnetic brakes as the primary braking mechanism. These brakes consist of an electromagnetic coil and a brake disc or plate. When the power to the motor is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field that attracts the brake disc or plate, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. The strength of the magnetic field and the design of the brake determine the stopping torque and speed, allowing for controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
2. Spring-Loaded Brakes: Some brake motors employ spring-loaded brakes. These brakes consist of a spring that applies pressure on the brake disc or plate to create friction and stop the rotation. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the spring is released, pressing the brake disc against a stationary surface and generating braking force. The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick engagement of the brake, resulting in rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is another technique used in brake motors to achieve controlled stopping. It involves converting the kinetic energy of the rotating equipment into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the motor acts as a generator, and the electrical energy generated by the rotating equipment is converted into heat through the braking system. This dissipation of energy slows down and stops the rotation of the equipment in a controlled manner.
4. Control Systems: Brake motors are often integrated with control systems that enable precise control over the braking process. These control systems allow for adjustable braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, depending on the specific requirements of the application. By adjusting these parameters, operators can achieve the desired level of control and stopping performance, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
5. Coordinated Motor and Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with careful consideration of the motor and brake compatibility. The motor's characteristics, such as torque, speed, and power rating, are matched with the braking system's capabilities to ensure optimal performance. This coordinated design ensures that the brake can effectively stop the motor within the desired time frame and with the necessary braking force, achieving controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
Overall, brake motors employ electromagnetic brakes, spring-loaded brakes, dynamic braking, and control systems to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment. These braking mechanisms, combined with coordinated motor and brake design, enable precise control over the stopping process, ensuring the safety of operators, protecting equipment from damage, and maintaining operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-03-30
China supplier Modern Carton Packed bldc hub electric 220V brake DC with gearbox motor vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
Product Description:
Gear Motor-Torque Table Allowance Torque Unit:Upside (N.m)/Belowside (kgf.cm)
•Gearhead and Intermediate gearhead are sold separately.
•Enter the reduction ratio into the blank() within the model name.
•The speed is calculated by dividing the motor's synchronous speed by the reduction ratio. The actual speed is 2%~20% less than the displayed value, depending on the size of the load.
•To reduce the speed beyond the reduction ratio in the following table, attach an intermediate gearhead (reduction ratio: 10) between the reducer and motor. In that case, the permissible torque is 20N.m.
|
Type Motor/Gearhead |
Gear Ratio |
3 |
3.6 |
5 |
6 |
7.5 |
9 |
12.5 |
15 |
18 |
25 |
30 |
36 |
50 |
60 |
75 |
90 |
100 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
|
Speed r/min |
866 |
722 |
520 |
433 |
346 |
288 |
208 |
173 |
144 |
104 |
86 |
72 |
52 |
43 |
34 |
28 |
26 |
21 |
17 |
14 |
|
| Z5D120-24GU-M(5GU180KB) |
5GU()RC/ 5GU()RT |
0.87 |
1.04 |
1.45 |
1.74 |
2.41 |
5.44 |
4.02 |
4.82 |
5.78 |
8.03 |
9.64 |
10.4 |
14.5 |
17.4 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
8.87 |
10.6 |
14.8 |
17.7 |
24.6 |
55.5 |
41.0 |
48.2 |
59.0 |
81.9 |
98.3 |
106 |
148 |
177 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
Dimensions(Unit:mm):
Company Information
FAQ
Q: What're your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What's your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Please contact us if you have detailed requests, thank you () /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brushless |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC, CCC, CE, RoHS, UL |
| Commutation: | Brushless |
| Transport Package: | Cnt |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can brake motors be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments?
Brake motors can indeed be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments, provided they are appropriately designed and protected against the specific conditions they will encounter. The adaptability of brake motors allows them to function effectively and safely in diverse operating environments. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors can be adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor settings:
- Indoor Adaptation: Brake motors intended for indoor use are typically designed to meet the specific requirements of indoor environments. They are often constructed with enclosures that protect the motor from dust, debris, and moisture commonly found indoors. These enclosures can be in the form of drip-proof (DP), totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC), or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) designs. The enclosures prevent contaminants from entering the motor and ensure reliable and efficient operation in indoor settings.
- Outdoor Adaptation: When brake motors are required for outdoor applications, they need to be adapted to withstand the challenges posed by outdoor conditions, such as temperature variations, moisture, and exposure to elements. Outdoor-rated brake motors are designed with additional protective measures to ensure their durability and performance. They may feature weatherproof enclosures, such as totally enclosed fan-cooled (TEFC) or totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) enclosures with added gaskets and seals to prevent water ingress. These enclosures provide effective protection against rain, snow, dust, and other outdoor elements, allowing the motor to operate reliably in outdoor environments.
- Environmental Sealing: Brake motors can be equipped with environmental seals to further enhance their adaptability for both indoor and outdoor use. These seals provide an additional layer of protection against the entry of moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Depending on the specific application requirements, the seals can be applied to the motor's shaft, housing, or other vulnerable areas to ensure proper sealing and prevent damage or performance degradation due to environmental factors.
- Corrosion Resistance: In certain outdoor environments or specific indoor settings with corrosive elements, brake motors can be designed with corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These specialized materials, such as stainless steel or epoxy coatings, provide protection against corrosion caused by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt air. Corrosion-resistant brake motors are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance in corrosive environments.
- Temperature Considerations: Brake motors must be adapted to handle the temperature ranges encountered in both indoor and outdoor environments. For indoor applications, motors may be designed to operate within a specific temperature range, ensuring reliable performance without overheating. Outdoor-rated brake motors may have additional cooling features, such as oversized cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat effectively and operate within acceptable temperature limits. Heating elements can also be incorporated to prevent condensation and maintain optimal operating temperatures in outdoor or highly humid indoor environments.
- IP Rating: In addition to the specific adaptations mentioned above, brake motors for both indoor and outdoor use are often assigned an Ingress Protection (IP) rating. The IP rating indicates the motor's level of protection against solid particles (first digit) and water ingress (second digit). The higher the IP rating, the greater the protection offered. IP ratings help users select brake motors that are suitable for their intended environment by considering factors such as dust resistance, water resistance, and overall environmental durability.
By incorporating appropriate enclosures, environmental seals, corrosion-resistant materials, temperature management features, and IP ratings, brake motors can be successfully adapted for use in both indoor and outdoor environments. These adaptations ensure that the motors are well-protected, perform reliably, and maintain their efficiency and longevity, regardless of the operating conditions they are exposed to.

How do brake motors contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling?
Brake motors play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. They provide several advantages that improve the overall performance and productivity of these systems. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling:
- Precise Control: Brake motors offer precise control over the movement of conveyor systems. The braking mechanism allows for quick and accurate stopping, starting, and positioning of the conveyor belt or other material handling components. This precise control ensures efficient operation, minimizing the time and effort required to handle materials and reducing the risk of damage or accidents.
- Speed Regulation: Brake motors can regulate the speed of conveyor systems, allowing operators to adjust the conveying speed according to the specific requirements of the materials being handled. This speed control capability enables efficient material flow, optimizing production processes and preventing bottlenecks or congestion. It also contributes to better synchronization with upstream or downstream processes, improving overall system efficiency.
- Load Handling: Brake motors are designed to handle varying loads encountered in material handling applications. They provide the necessary power and torque to move heavy loads along the conveyor system smoothly and efficiently. The braking mechanism ensures safe and controlled stopping even with substantial loads, preventing excessive wear or damage to the system and facilitating efficient material transfer.
- Energy Efficiency: Brake motors are engineered for energy efficiency, contributing to cost savings and sustainability in material handling operations. They are designed to minimize energy consumption during operation by optimizing motor efficiency, reducing heat losses, and utilizing regenerative braking techniques. Energy-efficient brake motors help lower electricity consumption, resulting in reduced operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Safety Enhancements: Brake motors incorporate safety features that enhance the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling by safeguarding personnel and equipment. They are equipped with braking systems that provide reliable stopping power, preventing unintended motion or runaway loads. Emergency stop functionality adds an extra layer of safety, allowing immediate halting of the system in case of emergencies or hazards, thereby minimizing the potential for accidents and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Reliability and Durability: Brake motors are constructed to withstand the demanding conditions of material handling environments. They are designed with robust components and built-in protection features to ensure reliable operation even in harsh or challenging conditions. The durability of brake motors reduces downtime due to motor failures or maintenance issues, resulting in improved system efficiency and increased productivity.
- Integration and Automation: Brake motors can be seamlessly integrated into automated material handling systems, enabling efficient and streamlined operations. They can be synchronized with control systems and sensors to optimize material flow, automate processes, and enable efficient sorting, routing, or accumulation of items. This integration and automation capability enhances system efficiency, reduces manual intervention, and enables real-time monitoring and control of the material handling process.
- Maintenance and Serviceability: Brake motors are designed for ease of maintenance and serviceability, which contributes to the overall efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. They often feature modular designs that allow quick and easy replacement of components, minimizing downtime during maintenance or repairs. Accessible lubrication points, inspection ports, and diagnostic features simplify routine maintenance tasks, ensuring that the motors remain in optimal working condition and maximizing system uptime.
By providing precise control, speed regulation, reliable load handling, energy efficiency, safety enhancements, durability, integration with automation systems, and ease of maintenance, brake motors significantly contribute to the efficiency of conveyor systems and material handling operations. Their performance and features optimize material flow, reduce downtime, enhance safety, lower operating costs, and improve overall productivity in a wide range of industries and applications.

How do brake motors ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment?
Brake motors are designed to ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment by employing specific braking mechanisms. These mechanisms are integrated into the motor to provide efficient and precise stopping capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors achieve controlled and rapid stopping:
1. Electromagnetic Brakes: Many brake motors utilize electromagnetic brakes as the primary braking mechanism. These brakes consist of an electromagnetic coil and a brake disc or plate. When the power to the motor is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field that attracts the brake disc or plate, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. The strength of the magnetic field and the design of the brake determine the stopping torque and speed, allowing for controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
2. Spring-Loaded Brakes: Some brake motors employ spring-loaded brakes. These brakes consist of a spring that applies pressure on the brake disc or plate to create friction and stop the rotation. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the spring is released, pressing the brake disc against a stationary surface and generating braking force. The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick engagement of the brake, resulting in rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is another technique used in brake motors to achieve controlled stopping. It involves converting the kinetic energy of the rotating equipment into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the motor acts as a generator, and the electrical energy generated by the rotating equipment is converted into heat through the braking system. This dissipation of energy slows down and stops the rotation of the equipment in a controlled manner.
4. Control Systems: Brake motors are often integrated with control systems that enable precise control over the braking process. These control systems allow for adjustable braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, depending on the specific requirements of the application. By adjusting these parameters, operators can achieve the desired level of control and stopping performance, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
5. Coordinated Motor and Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with careful consideration of the motor and brake compatibility. The motor's characteristics, such as torque, speed, and power rating, are matched with the braking system's capabilities to ensure optimal performance. This coordinated design ensures that the brake can effectively stop the motor within the desired time frame and with the necessary braking force, achieving controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
Overall, brake motors employ electromagnetic brakes, spring-loaded brakes, dynamic braking, and control systems to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment. These braking mechanisms, combined with coordinated motor and brake design, enable precise control over the stopping process, ensuring the safety of operators, protecting equipment from damage, and maintaining operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-03-29
China factory Carton Packed High Quality DC with gearbox 220V brake 125W electric motor vacuum pump engine
Product Description
Product Description:
Gear Motor-Torque Table Allowance Torque Unit:Upside (N.m)/Belowside (kgf.cm)
•Gearhead and Intermediate gearhead are sold separately.
•Enter the reduction ratio into the blank() within the model name.
•The speed is calculated by dividing the motor's synchronous speed by the reduction ratio. The actual speed is 2%~20% less than the displayed value, depending on the size of the load.
•To reduce the speed beyond the reduction ratio in the following table, attach an intermediate gearhead (reduction ratio: 10) between the reducer and motor. In that case, the permissible torque is 20N.m.
|
Type Motor/Gearhead |
Gear Ratio |
3 |
3.6 |
5 |
6 |
7.5 |
9 |
12.5 |
15 |
18 |
25 |
30 |
36 |
50 |
60 |
75 |
90 |
100 |
120 |
150 |
180 |
|
Speed r/min |
866 |
722 |
520 |
433 |
346 |
288 |
208 |
173 |
144 |
104 |
86 |
72 |
52 |
43 |
34 |
28 |
26 |
21 |
17 |
14 |
|
| Z5D120-24GU-M(5GU180KB) |
5GU()RC/ 5GU()RT |
0.87 |
1.04 |
1.45 |
1.74 |
2.41 |
5.44 |
4.02 |
4.82 |
5.78 |
8.03 |
9.64 |
10.4 |
14.5 |
17.4 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
8.87 |
10.6 |
14.8 |
17.7 |
24.6 |
55.5 |
41.0 |
48.2 |
59.0 |
81.9 |
98.3 |
106 |
148 |
177 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
Dimensions(Unit:mm):
Company Information
FAQ
Q: What're your main products?
A: We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc Gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors, Ac Motors and High Precision Planetary Gear Box etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q: How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed lifetime and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have a customized service for your standard motors?
A: Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q: Do you have an individual design service for motors?
A: Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mold developing cost and design charge.
Q: What's your lead time?
A: Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 15-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depend on the specific orders.
Please contact us if you have detailed requests, thank you () /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Industrial, Power Tools |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brushless |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC, CCC, CE, RoHS, UL |
| Commutation: | Brushless |
| Transport Package: | Cnt |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment?
Brake motors play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and controlled movement in equipment by providing reliable braking functionality. They work in coordination with the motor and other control systems to achieve precise control over the motion of the equipment. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment:
- Braking Capability: Brake motors are specifically designed to provide effective braking capability. When the power to the motor is cut off or when a braking signal is applied, the brake system engages, generating frictional forces that slow down and bring the equipment to a controlled stop. The brake torque generated by the motor helps prevent coasting or unintended movement, ensuring smooth and controlled deceleration.
- Quick Response Time: Brake motors are engineered to have a quick response time, meaning that the brake engages rapidly once the control signal is applied. This quick response time allows for prompt and precise control over the movement of the equipment. By minimizing the delay between the initiation of the braking action and the actual engagement of the brake, brake motors contribute to smooth and controlled movement.
- Adjustable Brake Torque: Brake motors often offer the ability to adjust the brake torque to suit the specific requirements of the equipment and application. The brake torque can be tailored to the load characteristics and operating conditions to achieve optimal braking performance. By adjusting the brake torque, brake motors ensure that the equipment decelerates smoothly and consistently, avoiding abrupt stops or jerky movements.
- Brake Release Mechanisms: In addition to providing braking action, brake motors incorporate mechanisms to release the brake when the equipment needs to resume motion. These release mechanisms can be controlled manually or automatically, depending on the application. The controlled release of the brake ensures that the equipment starts moving smoothly and gradually, allowing for controlled acceleration.
- Integration with Control Systems: Brake motors are integrated into the overall control systems of the equipment to achieve coordinated and synchronized movement. They work in conjunction with motor control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or servo systems, to precisely control the speed, acceleration, and deceleration of the equipment. By seamlessly integrating with the control systems, brake motors contribute to the smooth and controlled movement of the equipment.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Brake motors are designed and manufactured in compliance with safety standards and regulations. They undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure reliable and consistent braking performance. By adhering to safety standards, brake motors help prevent sudden or uncontrolled movements that could pose a safety risk and ensure the equipment operates within acceptable limits.
By providing effective braking capability, quick response time, adjustable brake torque, release mechanisms, integration with control systems, and compliance with safety standards, brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment. They enable precise control over the deceleration, stopping, and starting of the equipment, enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and overall performance.

How does a brake motor enhance safety in industrial and manufacturing settings?
In industrial and manufacturing settings, brake motors play a crucial role in enhancing safety by providing reliable braking and control mechanisms. These motors are specifically designed to address safety concerns and mitigate potential risks associated with rotating machinery and equipment. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors enhance safety in industrial and manufacturing settings:
1. Controlled Stopping: Brake motors offer controlled stopping capabilities, allowing for precise and predictable deceleration of rotating machinery. This controlled stopping helps prevent abrupt stops or sudden changes in motion, reducing the risk of accidents, equipment damage, and injury to personnel. By providing smooth and controlled stopping, brake motors enhance safety during machine shutdowns, emergency stops, or power loss situations.
2. Emergency Stop Functionality: Brake motors often incorporate emergency stop functionality as a safety feature. In case of an emergency or hazardous situation, operators can activate the emergency stop function to immediately halt the motor and associated machinery. This rapid and reliable stopping capability helps prevent accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment, providing an essential safety measure in industrial environments.
3. Load Holding Capability: Brake motors have the ability to hold loads in position when the motor is not actively rotating. This load holding capability is particularly important for applications where the load needs to be securely held in place, such as vertical lifting mechanisms or inclined conveyors. By preventing unintended movement or drift of the load, brake motors ensure safe operation and minimize the risk of uncontrolled motion that could lead to accidents or damage.
4. Overload Protection: Brake motors often incorporate overload protection mechanisms to safeguard against excessive loads. These protection features can include thermal overload protection, current limiters, or torque limiters. By detecting and responding to overload conditions, brake motors help prevent motor overheating, component failure, and potential hazards caused by overburdened machinery. This protection enhances the safety of personnel and prevents damage to equipment.
5. Failsafe Braking: Brake motors are designed with failsafe braking systems that ensure reliable braking even in the event of power loss or motor failure. These systems can use spring-loaded brakes or electromagnetic brakes that engage automatically when power is cut off or when a fault is detected. Failsafe braking prevents uncontrolled motion and maintains the position of rotating machinery, reducing the risk of accidents, injury, or damage during power interruptions or motor failures.
6. Integration with Safety Systems: Brake motors can be integrated into safety systems and control architectures to enhance overall safety in industrial settings. They can be connected to safety relays, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), or safety-rated drives to enable advanced safety functionalities such as safe torque off (STO) or safe braking control. This integration ensures that the brake motor operates in compliance with safety standards and facilitates coordinated safety measures across the machinery or production line.
7. Compliance with Safety Standards: Brake motors are designed and manufactured in compliance with industry-specific safety standards and regulations. These standards, such as ISO standards or Machinery Directive requirements, define the safety criteria and performance expectations for rotating machinery. By using brake motors that meet these safety standards, industrial and manufacturing settings can ensure a higher level of safety, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation.
8. Operator Safety: Brake motors also contribute to operator safety by reducing the risk of unintended movement or hazardous conditions. The controlled stopping and load holding capabilities of brake motors minimize the likelihood of unexpected machine behavior that could endanger operators. Additionally, the incorporation of safety features like emergency stop buttons or remote control options provides operators with convenient means to stop or control the machinery from a safe distance, reducing their exposure to potential hazards.
By providing controlled stopping, emergency stop functionality, load holding capability, overload protection, failsafe braking, integration with safety systems, compliance with safety standards, and operator safety enhancements, brake motors significantly enhance safety in industrial and manufacturing settings. These motors play a critical role in preventing accidents, injuries, and equipment damage, contributing to a safer working environment and ensuring the well-being of personnel.

What industries and applications commonly use brake motors?
Brake motors find wide-ranging applications across various industries that require controlled stopping, load holding, and precise positioning. Here's a detailed overview of the industries and applications commonly using brake motors:
1. Material Handling: Brake motors are extensively used in material handling equipment such as cranes, hoists, winches, and conveyors. These applications require precise control over the movement of heavy loads, and brake motors provide efficient stopping and holding capabilities, ensuring safe and controlled material handling operations.
2. Elevators and Lifts: The vertical movement of elevators and lifts demands reliable braking systems to hold the load in position during power outages or when not actively driving the movement. Brake motors are employed in elevator systems to ensure passenger safety and prevent unintended movement or freefall of the elevator car.
3. Machine Tools: Brake motors are used in machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, drilling machines, and grinders. These applications often require precise positioning and rapid stopping of rotating spindles or cutting tools. Brake motors provide the necessary control and safety measures for efficient machining operations.
4. Conveyor Systems: Conveyor systems in industries like manufacturing, logistics, and warehouses utilize brake motors to achieve accurate control over the movement of goods. Brake motors enable smooth acceleration, controlled deceleration, and precise stopping of conveyor belts, ensuring proper material flow and minimizing the risk of collisions or product damage.
5. Crushers and Crushers: In industries such as mining, construction, and aggregates, brake motors are commonly used in crushers and crushers. These machines require rapid and controlled stopping to prevent damage caused by excessive vibration or unbalanced loads. Brake motors provide the necessary braking force to halt the rotation of crusher components quickly.
6. Robotics and Automation: Brake motors play a vital role in robotics and automation systems that require precise movement control and positioning. They are employed in robotic arms, automated assembly lines, and pick-and-place systems to achieve accurate and repeatable movements, ensuring seamless operation and high productivity.
7. Printing and Packaging: Brake motors are utilized in printing presses, packaging machines, and labeling equipment. These applications require precise control over the positioning of materials, accurate registration, and consistent stopping during printing or packaging processes. Brake motors ensure reliable performance and enhance the quality of printed and packaged products.
8. Textile Machinery: Brake motors are commonly found in textile machinery such as spinning machines, looms, and textile printing equipment. These applications demand precise control over yarn tension, fabric movement, and position holding. Brake motors offer the necessary braking force and control for smooth textile manufacturing processes.
9. Food Processing: Brake motors are employed in food processing equipment, including mixers, slicers, extruders, and dough handling machines. These applications require precise control over mixing, slicing, and shaping processes, as well as controlled stopping to ensure operator safety and prevent product wastage.
These are just a few examples, and brake motors are utilized in numerous other industries and applications where controlled stopping, load holding, and precise positioning are essential. The versatility and reliability of brake motors make them a preferred choice in various industrial sectors, contributing to enhanced safety, productivity, and operational control.


editor by CX 2024-03-28
China Professional 25W High Torque AC Gear Motor 220V with Brake vacuum pump belt
Product Description
A. Specification of 25W High Torque AC Gear Motor 220V with Brake:
1. Voltage: 110/220/380V
2. Speed: 2-600RPM
3. Torque: 4.4-80Kgf.cm
4. Output Power: 25W
5. Gearbox Ratio: 1:3 to 1: 750
6. Gearbox Diameter: 80mm
7. Gearbox Length: 32-43.5mm
8. Motor Length: 85mm
9. Shaft Diameter: 10mm
10. Motor Weight: 2Kg
11. Gearbox Weight: 0.43-0.61Kg
Note: The data sheet is only for reference, We can make the motor according to your requirement after Evaluation
B. Company Capacity
HangZhou CHINAMFG Motor Co. Ltd is a manufacturer and exporter of various of motors with over 10 years experience.
Our product ranges include:
1) DC Brush motor: 6-130mm diameter, 0.01-1000W output power
2) DC Spur Gear Motor: 12-110mm diameter, 0.1-300W output power
3) DC Planeary Gear Motor: 10-82mm diameter, 0.1-100W output power
4) Brushless DC Motor: 28-110mm, 5-1500W output power
5) Stepper Motor: NEMA 08 to NEMA 43, Can with gearbox and lead screw
6) Servo Motor: 42mm to 130mm diameter, 50-4000w
7) AC Gear Motor: 49 to 100mm diameter, 6-140 output power
1. Production Line:
2. Testing Equipment:
3. Certificates:
4. Customer Visits:
6. FAQ:
Q: What's your main products?
A:We currently produce Brushed Dc Motors, Brushed Dc gear Motors, Planetary Dc Gear Motors, Brushless Dc Motors, Stepper motors and Ac Motors etc. You can check the specifications for above motors on our website and you can email us to recommend needed motors per your specification too.
Q:How to select a suitable motor?
A:If you have motor pictures or drawings to show us, or you have detailed specs like voltage, speed, torque, motor size, working mode of the motor, needed life time and noise level etc, please do not hesitate to let us know, then we can recommend suitable motor per your request accordingly.
Q: Do you have customized service for your standard motors?
A:Yes, we can customize per your request for the voltage, speed, torque and shaft size/shape. If you need additional wires/cables soldered on the terminal or need to add connectors, or capacitors or EMC we can make it too.
Q:Do you have individual design service for motors?
A:Yes, we would like to design motors individually for our customers, but it may need some mould charge and design charge.
Q:Can I have samples for testing first?
A:Yes, definitely you can. After confirmed the needed motor specs, we will quote and provide a proforma invoice for samples, once we get the payment, we will get a PASS from our account department to proceed samples accordingly.
Q:How do you make sure motor quality?
A:We have our own inspection procedures: for incoming materials, we have signed sample and drawing to make sure qualified incoming materials; for production process, we have tour inspection in the process and final inspection to make sure qualified products before shipping.
Q:What's your lead time?
A:Generally speaking, our regular standard product will need 25-30days, a bit longer for customized products. But we are very flexible on the lead time, it will depends on the specific orders
Q:What's your payment term?
A:For all our new customers, we will need 40% deposite, 60% paid before shipment.
Q:When will you reply after got my inquiries?
A:We will response within 24 hours once get your inquires.
Q:How can I trust you to make sure my money is safe?
A:We are certified by the third party SGS and we have exported to over 85 countries up to June.2017. You can check our reputation with our current customers in your country (if our customers do not mind), or you can order via alibaba to get trade assurance from alibaba to make sure your money is safe.
Q:What's the minimum order quantity?
A:Our minimum order quantity depends on different motor models, please email us to check. Also, we usually do not accept personal use motor orders.
Q:What's your shipping method for motors?
A:For samples and packages less than 100kg, we usually suggest express shipping; For heavy packages, we usually suggest air shipping or sea shipping. But it all depends on our customers' needs.
Q:What certifications do you have?
A:We currently have CE and ROSH certifications.
Q:Can you send me your price list?
A:Since we have hundreds of different products, and price varies per different specifications, we are not able to offer a price list. But we can quote within 24 hours once got your inquirues to make sure you can get the price in time.
Q:Can I visit your company?
A:Yes, welcome to visit our company, but please let us know at least 2 weeks in advance to help us make sure no other meetings during the day you visit us. Thanks!
Weclome contact with us if have any questions about this motor or other products! /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Universal, Household Appliances, Power Tools, Others |
|---|---|
| Operating Speed: | Low Speed |
| Function: | Driving |
| Casing Protection: | Closed Type |
| Structure and Working Principle: | Brush |
| Type: | AC Gear Motor |
| Samples: |
US$ 70/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Are there any emerging trends in brake motor technology, such as digital control?
Yes, there are emerging trends in brake motor technology that are shaping the future of this field. One such trend is the adoption of digital control systems, which offer several advantages over traditional control methods. These advancements in digital control are revolutionizing brake motor technology and unlocking new possibilities for improved performance, efficiency, and integration within industrial processes. Here's a detailed explanation of the emerging trends in brake motor technology, including the shift towards digital control:
- Digital Control Systems: Digital control systems are becoming increasingly prevalent in brake motor technology. These systems utilize advanced microprocessors, sensors, and software algorithms to provide precise control, monitoring, and diagnostics. Digital control enables enhanced motor performance, optimized energy efficiency, and improved operational flexibility. It allows for seamless integration with other digital systems, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or industrial automation networks, facilitating intelligent and interconnected manufacturing processes.
- Intelligent Motor Control: The integration of digital control systems with brake motors enables intelligent motor control capabilities. These systems use sensor feedback and real-time data analysis to dynamically adjust motor parameters, such as speed, torque, and braking force, based on the changing operating conditions. Intelligent motor control optimizes motor performance, minimizes energy consumption, and enhances overall system efficiency. It also enables predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring motor health and providing early warnings for potential faults or failures.
- Network Connectivity and Industry 4.0: Brake motors are increasingly designed to be part of interconnected networks in line with the principles of Industry 4.0. With digital control systems, brake motors can be connected to industrial networks, enabling real-time data exchange, remote monitoring, and control. This connectivity facilitates centralized monitoring and management of multiple brake motors, improves system coordination, and enables predictive analytics for proactive decision-making. It also allows for seamless integration with other smart devices and systems, paving the way for advanced automation and optimization in manufacturing processes.
- Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance: Digital control systems in brake motors enable advanced condition monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Sensors integrated into the motor can collect data on parameters such as temperature, vibration, and load conditions. This data is processed and analyzed in real-time, allowing for early detection of potential issues or performance deviations. By implementing predictive maintenance strategies, manufacturers can schedule maintenance activities more efficiently, reduce unplanned downtime, and optimize the lifespan and reliability of brake motors.
- Energy Efficiency Optimization: Digital control systems provide enhanced opportunities for optimizing energy efficiency in brake motors. These systems can intelligently adjust motor parameters based on load demand, operating conditions, and energy consumption patterns. Advanced algorithms and control techniques optimize the motor's energy usage, reducing power wastage and maximizing overall energy efficiency. Digital control also enables integration with energy management systems, allowing for better monitoring and control of energy consumption across the entire manufacturing process.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: The integration of digital control systems with brake motors opens up possibilities for leveraging data analytics and machine learning techniques. By collecting and analyzing large volumes of motor performance data, manufacturers can gain valuable insights into process optimization, fault detection, and performance trends. Machine learning algorithms can be applied to identify patterns, predict motor behavior, and optimize control strategies. This data-driven approach enhances decision-making, improves productivity, and enables continuous improvement in manufacturing processes.
In summary, emerging trends in brake motor technology include the adoption of digital control systems, intelligent motor control, network connectivity, condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, energy efficiency optimization, and data analytics. These trends are driving innovation in brake motor technology, improving performance, efficiency, and integration within manufacturing processes. As digital control becomes more prevalent, brake motors are poised to play a vital role in the era of smart manufacturing and industrial automation.

What maintenance practices are essential for extending the lifespan of a brake motor?
Maintaining a brake motor properly is crucial for extending its lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. Regular maintenance practices help prevent premature wear, identify potential issues, and address them promptly. Here are some essential maintenance practices for extending the lifespan of a brake motor:
- Cleanliness: Keeping the brake motor clean is important to prevent the accumulation of dirt, dust, or debris that can affect its performance. Regularly inspect the motor and clean it using appropriate cleaning methods and materials, ensuring that the power is disconnected before performing any cleaning tasks.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of the brake motor's moving parts is essential to minimize friction and reduce wear and tear. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding the type of lubricant to use and the frequency of lubrication. Ensure that the lubrication points are accessible and apply the lubricant in the recommended amounts.
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections of the brake motor are necessary to identify any signs of damage, loose connections, or abnormal wear. Check for any loose or damaged components, such as bolts, cables, or connectors. Inspect the brake pads or discs for wear and ensure they are properly aligned. If any issues are detected, take appropriate action to address them promptly.
- Brake Adjustment: Periodically check and adjust the brake mechanism of the motor to ensure it maintains proper braking performance. This may involve adjusting the brake pads, ensuring proper clearance, and verifying that the braking force is sufficient. Improper brake adjustment can lead to excessive wear, reduced stopping power, or safety hazards.
- Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring the operating temperature of the brake motor is important to prevent overheating and thermal damage. Ensure that the motor is not subjected to excessive ambient temperatures or overloaded conditions. If the motor becomes excessively hot, investigate the cause and take corrective measures, such as improving ventilation or reducing the load.
- Vibration Analysis: Periodic vibration analysis can help detect early signs of mechanical problems or misalignment in the brake motor. Using specialized equipment or vibration monitoring systems, measure and analyze the motor's vibration levels. If abnormal vibrations are detected, investigate and address the underlying issues to prevent further damage.
- Electrical Connections: Regularly inspect the electrical connections of the brake motor to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or faulty connections can lead to power issues, motor malfunctions, or electrical hazards. Tighten any loose connections and clean any corrosion using appropriate methods and materials.
- Testing and Calibration: Perform periodic testing and calibration of the brake motor to verify its performance and ensure it operates within the specified parameters. This may involve conducting load tests, verifying braking force, or checking the motor's speed and torque. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines or consult with qualified technicians for proper testing and calibration procedures.
- Documentation and Record-keeping: Maintain a record of all maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and any relevant information related to the brake motor. This documentation helps track the maintenance history, identify recurring issues, and plan future maintenance tasks effectively. It also serves as a reference for warranty claims or troubleshooting purposes.
- Professional Servicing: In addition to regular maintenance tasks, consider scheduling professional servicing and inspections by qualified technicians. They can perform comprehensive checks, identify potential issues, and perform specialized maintenance procedures that require expertise or specialized tools. Professional servicing can help ensure thorough maintenance and maximize the lifespan of the brake motor.
By following these essential maintenance practices, brake motor owners can enhance the lifespan of the motor, reduce the risk of unexpected failures, and maintain its optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only extends the motor's lifespan but also contributes to safe operation, energy efficiency, and overall reliability.

How do brake motors ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment?
Brake motors are designed to ensure controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment by employing specific braking mechanisms. These mechanisms are integrated into the motor to provide efficient and precise stopping capabilities. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors achieve controlled and rapid stopping:
1. Electromagnetic Brakes: Many brake motors utilize electromagnetic brakes as the primary braking mechanism. These brakes consist of an electromagnetic coil and a brake disc or plate. When the power to the motor is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the electromagnetic coil generates a magnetic field that attracts the brake disc or plate, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. The strength of the magnetic field and the design of the brake determine the stopping torque and speed, allowing for controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
2. Spring-Loaded Brakes: Some brake motors employ spring-loaded brakes. These brakes consist of a spring that applies pressure on the brake disc or plate to create friction and stop the rotation. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the spring is released, pressing the brake disc against a stationary surface and generating braking force. The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick engagement of the brake, resulting in rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
3. Dynamic Braking: Dynamic braking is another technique used in brake motors to achieve controlled stopping. It involves converting the kinetic energy of the rotating equipment into electrical energy, which is dissipated as heat through a resistor or regenerative braking system. When the power is cut off or the motor is de-energized, the motor acts as a generator, and the electrical energy generated by the rotating equipment is converted into heat through the braking system. This dissipation of energy slows down and stops the rotation of the equipment in a controlled manner.
4. Control Systems: Brake motors are often integrated with control systems that enable precise control over the braking process. These control systems allow for adjustable braking torque, response time, and braking profiles, depending on the specific requirements of the application. By adjusting these parameters, operators can achieve the desired level of control and stopping performance, ensuring both safety and operational efficiency.
5. Coordinated Motor and Brake Design: Brake motors are designed with careful consideration of the motor and brake compatibility. The motor's characteristics, such as torque, speed, and power rating, are matched with the braking system's capabilities to ensure optimal performance. This coordinated design ensures that the brake can effectively stop the motor within the desired time frame and with the necessary braking force, achieving controlled and rapid stopping of the rotating equipment.
Overall, brake motors employ electromagnetic brakes, spring-loaded brakes, dynamic braking, and control systems to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of rotating equipment. These braking mechanisms, combined with coordinated motor and brake design, enable precise control over the stopping process, ensuring the safety of operators, protecting equipment from damage, and maintaining operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-03-27
China factory 220V 5.5kw 7.02nm 3000rpm 180st-M27020 Single-Phase AC Servo Motor with Optional Power off Brake vacuum pump
Product Description
220V 5.5KW 7.02Nm 3000rpm 180ST-M27571 Single-Phase AC Servo Motor with Optional Power off Brake
Product Description
Features:
Motor frame (mm): 60, 80, 110, 130
Rated speed (rpm): 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000
Power off brake: optional
Insulation level: F
Installation: flange-mounted
Environmental temperature: 0 to 55 degrees
Rated torque (Nm): 0.33 to 17.8
Maximum speed (rpm): 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000, 6000
Rated power (Kw): 0.1 to 3.1
Number of pole pairs: 5
Protection level: sealed, self-cooling IP65
Operation voltage of matched amplifier (VAC): 220
Environmental humidity: lower than 90% (condensation free)
Naming convention of series LDD power servo motor
|
110 |
ST |
M |
042 |
15 |
30 |
L |
M1 |
D |
D | Z |
/C |
|
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) | (11) |
(12) |
(1) Motor frame No.
(2) AC permanent magnet synchronization servo motor
(3) Feedback component type
(4) Rated torque: three-digit number × 0.1Nm
(5) Rated speed: two-digit number × 100rpm
(6) Maximum speed: two-digit number × 100rpm
(7) Operation voltage of matched amplifier: 220
(8) Encoder code
(9) Medium inertia
(10) The highest speed characteristic
(11) Power-off brake is mounted
(12) Keyway code; if there is no key, there is no code
Cooperation Brand
Company Profile
| Application: | CNC Machine |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Constant Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Single-Phase |
| Function: | Control |
| Casing Protection: | Protection Type |
| Number of Poles: | 5 |
| Samples: |
US$ 200/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How do brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment?
Brake motors play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and controlled movement in equipment by providing reliable braking functionality. They work in coordination with the motor and other control systems to achieve precise control over the motion of the equipment. Here's a detailed explanation of how brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment:
- Braking Capability: Brake motors are specifically designed to provide effective braking capability. When the power to the motor is cut off or when a braking signal is applied, the brake system engages, generating frictional forces that slow down and bring the equipment to a controlled stop. The brake torque generated by the motor helps prevent coasting or unintended movement, ensuring smooth and controlled deceleration.
- Quick Response Time: Brake motors are engineered to have a quick response time, meaning that the brake engages rapidly once the control signal is applied. This quick response time allows for prompt and precise control over the movement of the equipment. By minimizing the delay between the initiation of the braking action and the actual engagement of the brake, brake motors contribute to smooth and controlled movement.
- Adjustable Brake Torque: Brake motors often offer the ability to adjust the brake torque to suit the specific requirements of the equipment and application. The brake torque can be tailored to the load characteristics and operating conditions to achieve optimal braking performance. By adjusting the brake torque, brake motors ensure that the equipment decelerates smoothly and consistently, avoiding abrupt stops or jerky movements.
- Brake Release Mechanisms: In addition to providing braking action, brake motors incorporate mechanisms to release the brake when the equipment needs to resume motion. These release mechanisms can be controlled manually or automatically, depending on the application. The controlled release of the brake ensures that the equipment starts moving smoothly and gradually, allowing for controlled acceleration.
- Integration with Control Systems: Brake motors are integrated into the overall control systems of the equipment to achieve coordinated and synchronized movement. They work in conjunction with motor control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) or servo systems, to precisely control the speed, acceleration, and deceleration of the equipment. By seamlessly integrating with the control systems, brake motors contribute to the smooth and controlled movement of the equipment.
- Compliance with Safety Standards: Brake motors are designed and manufactured in compliance with safety standards and regulations. They undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure reliable and consistent braking performance. By adhering to safety standards, brake motors help prevent sudden or uncontrolled movements that could pose a safety risk and ensure the equipment operates within acceptable limits.
By providing effective braking capability, quick response time, adjustable brake torque, release mechanisms, integration with control systems, and compliance with safety standards, brake motors ensure smooth and controlled movement in equipment. They enable precise control over the deceleration, stopping, and starting of the equipment, enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and overall performance.

How do manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors?
Manufacturers employ various processes and measures to ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors. These processes involve rigorous testing, adherence to industry standards, quality control procedures, and continuous improvement initiatives. Here's a detailed explanation of how manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors:
- Design and Engineering: Manufacturers invest considerable effort in the design and engineering phase of brake motors. They employ experienced engineers and designers who follow industry best practices and utilize advanced design tools to develop motors with robust and reliable braking systems. Thorough analysis, simulations, and prototyping are conducted to optimize the motor's performance, efficiency, and safety features.
- Material Selection: High-quality materials are chosen for the construction of brake motors. Manufacturers carefully select components such as motor windings, brake discs, brake pads, and housing materials to ensure durability, heat resistance, and optimal friction characteristics. The use of quality materials enhances the motor's reliability and contributes to its long-term performance.
- Manufacturing Processes: Stringent manufacturing processes are implemented to ensure consistent quality and reliability. Manufacturers employ advanced machinery and automation techniques for precision assembly and production. Strict quality control measures are applied at each stage of manufacturing to detect and rectify any defects or deviations from specifications.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Brake motors undergo comprehensive testing and quality assurance procedures before they are released to the market. These tests include performance testing, load testing, endurance testing, and environmental testing. Manufacturers verify that the motors meet or exceed industry standards and performance specifications. Additionally, they conduct safety tests to ensure compliance with applicable safety regulations and standards.
- Certifications and Compliance: Manufacturers seek certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations. This may include certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or certifications specific to the motor industry, such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards. Compliance with these standards demonstrates the manufacturer's commitment to producing high-quality and reliable brake motors.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Manufacturers implement robust quality control processes throughout the production cycle. This includes inspection of raw materials, in-process inspections during manufacturing, and final inspections before shipment. Quality control personnel conduct visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance evaluations to ensure that each brake motor meets the specified quality criteria.
- Continuous Improvement: Manufacturers prioritize continuous improvement initiatives to enhance the quality and reliability of brake motors. They actively seek customer feedback, monitor field performance, and conduct post-production evaluations to identify areas for improvement. This feedback loop helps manufacturers refine their designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control procedures, leading to increased reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Support and Warranty: Manufacturers provide comprehensive customer support and warranty programs for their brake motors. They offer technical assistance, troubleshooting guides, and maintenance recommendations to customers. Warranty coverage ensures that any manufacturing defects or malfunctions are addressed promptly, bolstering customer confidence in the quality and reliability of the brake motors.
By employing robust design and engineering processes, meticulous material selection, stringent manufacturing processes, comprehensive testing and quality assurance procedures, certifications and compliance with industry standards, rigorous quality control and inspection measures, continuous improvement initiatives, and dedicated customer support and warranty programs, manufacturers ensure the quality and reliability of brake motors. These measures contribute to the production of high-performance motors that meet the safety, durability, and performance requirements of industrial and manufacturing applications.

Can you explain the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery?
The primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping and holding of loads. A brake motor combines the functionality of an electric motor and a braking system into a single unit, offering convenience and efficiency in various industrial applications. Here's a detailed explanation of the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery:
1. Controlled Stopping: One of the main purposes of a brake motor is to achieve controlled and rapid stopping of machinery. When power is cut off or the motor is turned off, the braking mechanism in the brake motor engages, creating friction and halting the rotation of the motor shaft. This controlled stopping is crucial in applications where precise and quick stopping is required to ensure the safety of operators, prevent damage to equipment, or maintain product quality. Industries such as material handling, cranes, and conveyors rely on brake motors to achieve efficient and controlled stopping of loads.
2. Load Holding: Brake motors are also designed to hold loads in a stationary position when the motor is not actively rotating. The braking mechanism in the motor engages when the power is cut off, preventing any unintended movement of the load. Load holding is essential in applications where it is necessary to maintain the position of the machinery or prevent the load from sliding or falling. For instance, in vertical applications like elevators or lifts, brake motors hold the load in place when the motor is not actively driving the movement.
3. Safety and Emergency Situations: Brake motors play a critical role in ensuring safety and mitigating risks in machinery. In emergency situations or power failures, the braking system of a brake motor provides an immediate response, quickly stopping the rotation of the motor shaft and preventing any uncontrolled movement of the load. This rapid and controlled stopping enhances the safety of operators and protects both personnel and equipment from potential accidents or damage.
4. Precision and Positioning: Brake motors are utilized in applications that require precise positioning or accurate control of loads. The braking mechanism allows for fine-tuned control, enabling operators to position machinery or loads with high accuracy. Industries such as robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines rely on brake motors to achieve precise movements, ensuring proper alignment, accuracy, and repeatability. The combination of motor power and braking functionality in a brake motor facilitates intricate and controlled operations.
Overall, the primary purpose of a brake motor in machinery is to provide controlled stopping, load holding, safety in emergency situations, and precise positioning. By integrating the motor and braking system into a single unit, brake motors streamline the operation and enhance the functionality of various industrial applications. Their reliable and efficient braking capabilities contribute to improved productivity, safety, and operational control in machinery and equipment.


editor by CX 2023-11-17